Oligohydramnios
Oligohydramnios
It is a condition in pregnancy characterized by a deficiency of amniotic fluid.
It is an extremely rare condition where the liquor amnii is deficient in amount to the extent of less than 200 mL at term.
Sonographically, it is Defined when the maximum vertical pocket of liquor is less than <2cm or when amniotic fluid index (AFI) is less than 5 cm (less than 5 percentile). With AFI less than 5 cm (below 5th percentile) or more than 24 cm (above 95th percentile) was considered abnormal at gestational age, from 28 to 40 weeks. Absence of any measurable pocket of amniotic fluid is defined as Anhydramnios.
Etiology
The exact cause is unknown. It is associated with:
1. Fetal conditions
- Fetal chromosomal or structural anomalies
- Renal agenesis
- Intrauterine infection
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
- Drugs: PG inhibitors, ACE inhibitors
- Obstructed uropathy
- Spontaneous rupture of the membrane
- Post maturity
- Decrease of foetal urine formation.
- Amnion nodosum (failure of secretion by the cells of the amnion covering the placenta).
2. Maternal conditions:
- Hypertensive disorders
- Uteroplacental insufficiency
- Dehydration
- Idiopathic.
Clinical Features
- Uterine size is much smaller than period of gestation.
- Less foetal movements.
- Breech presentation is common
- Evidence of foetal growth retardation and deformity.
- During labour thick meconium is passed.
- Ultrasonography shows absence of amniotic fluid pockets greater than 1 cm. in vertical plane. Renal abnormality may be visible.
Diagnosis
- Uterine size is much smaller than the period of amenorrhea
- Less fetal movements
- The uterus is “full of fetus” because of scanty liquor
- Malpresentation (breech) is common
- Evidences of intrauterine growth retardation of the fetus
- Sonographic diagnosis is made when largest liquor pool is less than 2 cm. Ultrasound visualization is done following amnioinfusion of 300 mL of warm saline solution
- Visualization of normal filling and emptying of fetal bladder essentially rules out urinary tract abnormality.
- Oligohydramnios with fetal symmetric growth restriction is associated with increased chromosomal abnormality
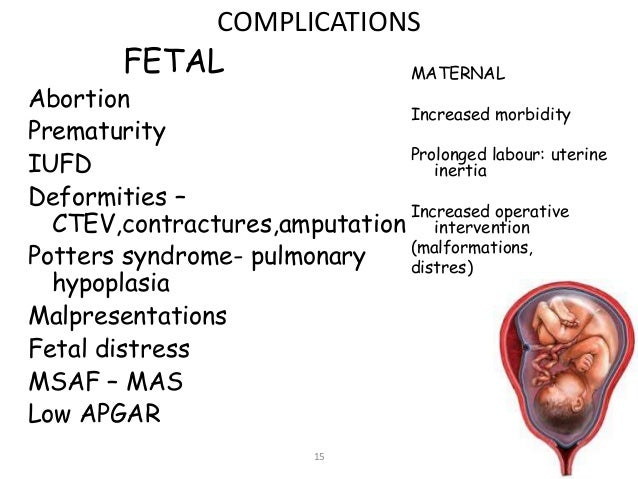
Complication-
Fetal-
- Abortion
- Deformity due to intra-amniotic adhesions or due to compression. The deformities include alteration in shape of the skull, wry neck, club foot, or even amputation of the limb
- Fetal pulmonary hypoplasia (may be the cause or effect)
- Cord compression
- High fetal mortality.
Maternal-
- Prolonged labor due to inertia
- Increased operative interference due to malpresentation. The sum effect may lead to increased maternal morbidity.
Treatment-
- A Cochrane review concluded that “simple maternal hydration appears to increase amniotic fluid volume and may be beneficial in the management of oligohydramnios and prevention of oligohydramnios during labour or prior to external cephalic version.
- In severe case oligohydramnios may be treated with amnioinfusion during labour to prevent umbilical cord compression.
- In case of foetal deformity and placental insufficiency pregnancy is terminated and vaginal delivery is favoured.