Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
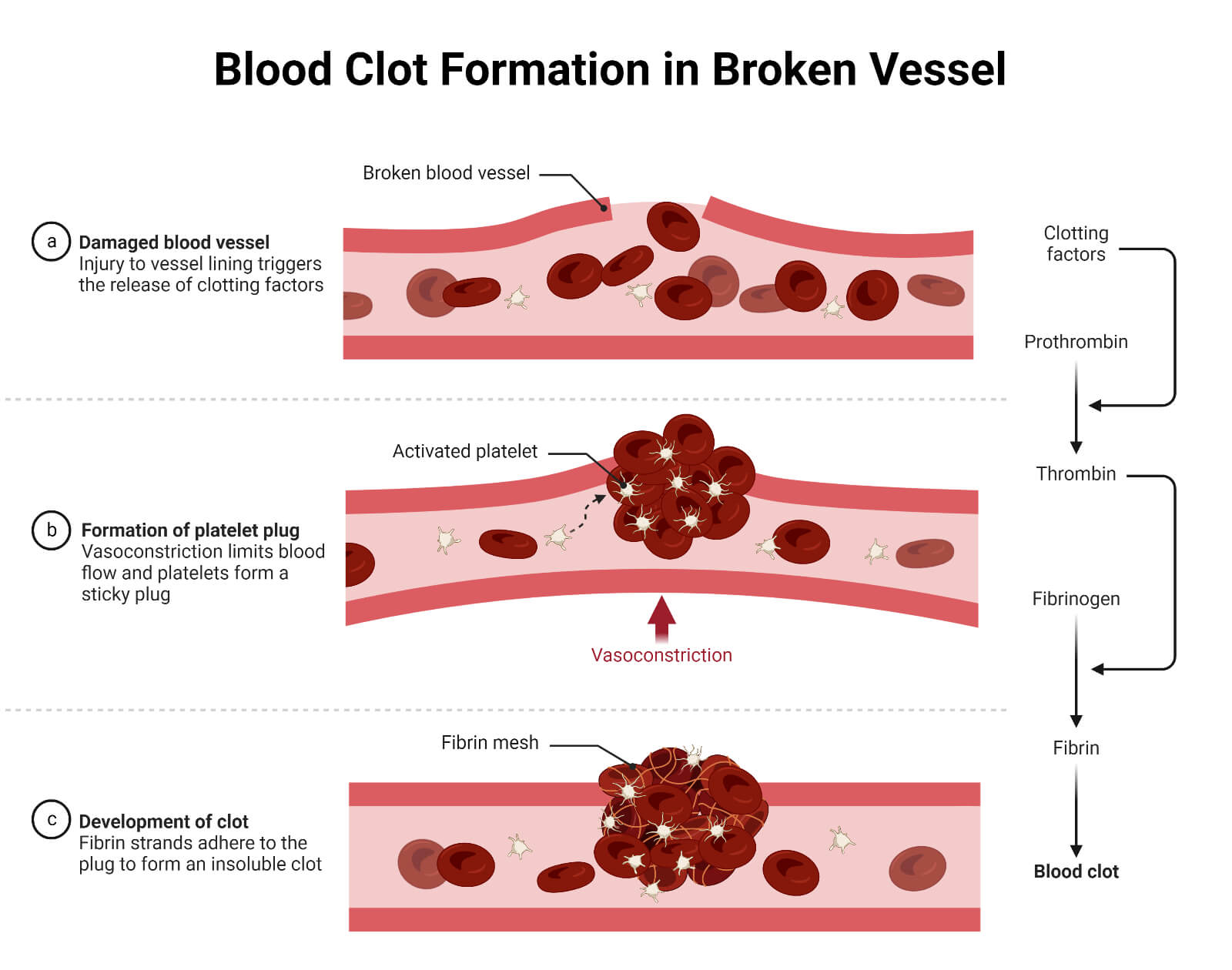
Coagulation of Blood
Coagulation of Blood
The process in which blood loses its fluidity and becomes a jelly-like mass few minutes after it ...


APPLIED ANATOMY & APPLIED PHYSIOLOGY BSc Nursing I Semester Supp Examination June 2024
6-06-2024 ...

Immunity
Immunity-
Immunity is defined as the capacity of the body to resist pathogenic agents. It is the ability of body to resist the entry...

Nervous system
Nervous system
Nervous system controls all activity of the body it is quicker than the other control system in the body like– end...
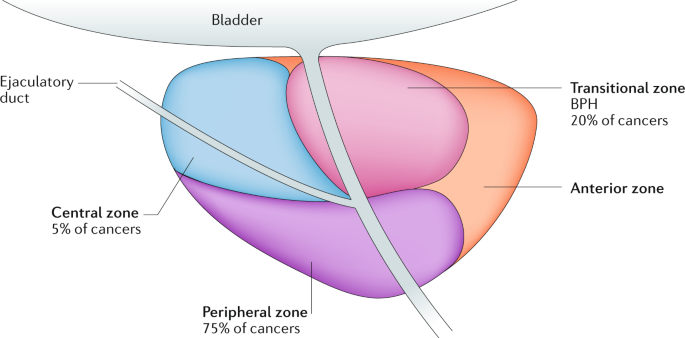
Prostate Gland
Prostate Gland-Human prostate gland weighs about 40 g. It consists of 20 to 30 separate glands, which open separa...

Adrenal gland
Adrenal gland
There are two adrenal glands, one situated on the upper pole of each kidney (so called suprarenal glands) enclosed wit...
##adrenal gland #nursing awareness

Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid is an endocrine gland situated at the root of the neck on either side of the trachea at the level of the 5th, 6th and 7th cervical and 1st thorac...

Pituitary gland
The endocrine system consists of a number of distinct glands and some tissues in other organs. Although the hypothalamus is classified as a part of the brain and not as an endocrine gland it con...

Blood vessels
Blood vessels
Blood vessels are part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arter...
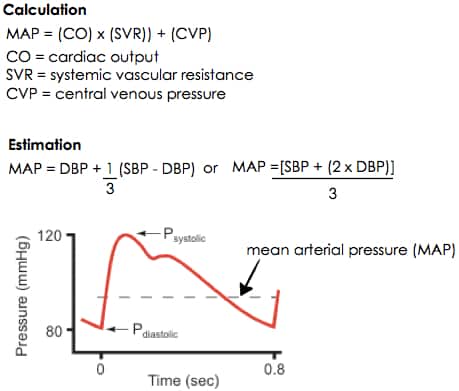
Arterial Blood Pressure
Arterial Blood Pressure-
The pressure is exerted when blood flows through the arteries. Generally, the term ‘blood pressure’ refers to arterial blood press...
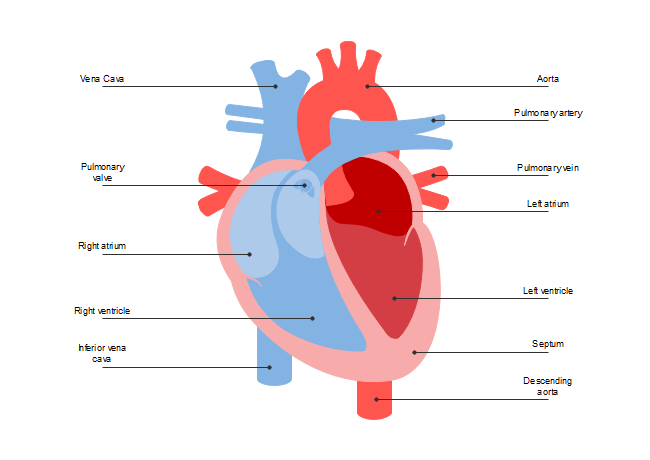
The cardiovascular system
Heart
Heart is a hollow muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the circulatory system. It is situated in between two lungs in th...
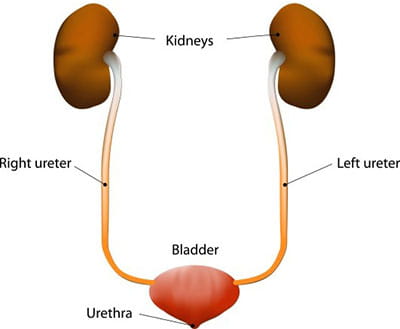
The urinary system
The urinary system is one of the excretory systems of the body. It consists of the following structures-
2 kidneys, which secrete urine
2 ureters, which convey the u...
Large Intestine
Large Intestine-
This is about 1.5 metres long, beginning at the caecum in the right iliac fossa and terminating at the rectum and anal canal deep in the pelvis.
...

Pancreas
Pancreas
Pancreas is a dual organ having two functions, namely endocrine function and exocrine function. Endocrine function is concerned with the production of hormone...

Gall bladder
Gall bladder
The gall bladder is a pear-shaped sac attached to the posterior surface of the liver by connective tissue. It has a fundus or expanded end, a body or main...

liver
The liver is the largest gland in the body, weighing between 1 and 2.3 kg. It is situated in the upper part of the abdominal cavity occupying the greater part of the right hypochondriac region, ...
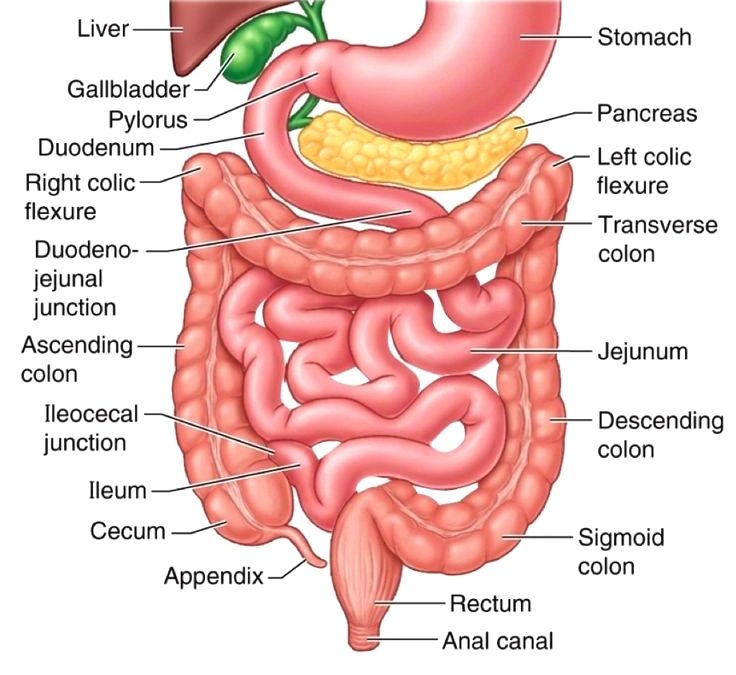
Small intestine
Small intestine-
Small intestine is the part of gastrointestinal (GI) tract, extending between the pyloric sphincter of stomach and ileocecal valve, which opens into l...

Stomach
Stomach-
Stomach is a hollow organ situated just below the diaphragm on the left side in the abdominal cavity. Volume of empty stomach is 50mL. Under normal conditions...
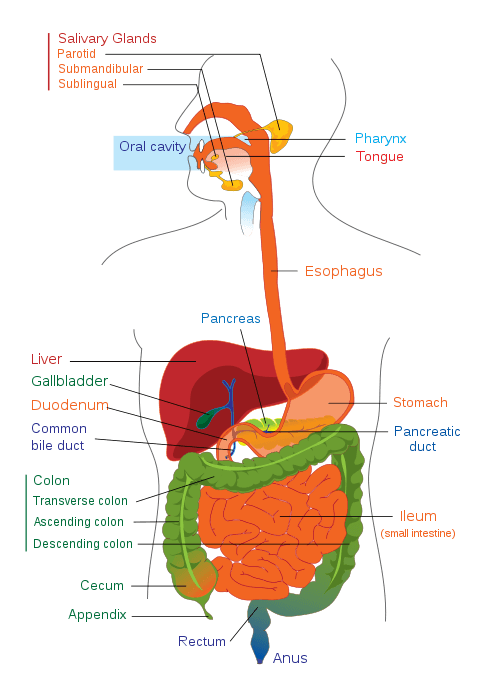
Introduction to Digestive System
Digestive System-
Digestive system is made up of gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) or alimentary canal and accessory organs, which help in the process of digestion and...


Salivary Gland
Salivary Gland- The saliva is secreted by three pairs of major (larger) salivary glands and some minor (small) salivary glands.
Major glands are-...

Blood
Circulatory system is a network consisting of blood, blood vessels and the heart.
Circulatory system is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the hea...

Respiratory Organs
Respiratory Organs-
The respiratory system is the set of organs that allows a person to breath and exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body.
Ex...

Meiosis
Meiosis-
The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced.
Diploid (2n) To Haploid (n)

Cell Division-Mitosis
CELL DIVISION-
Cell division is a very important process in all living organisms. During the division of a cell, DNA replication and cell growth also take place. All t...

Blood Groups
Blood Groups-
The discovery of blood groups by the Austrian Scientist Karl Landsteiner, in 1901. He was honored with Nobel Prize in 1930 for this discovery.More ...
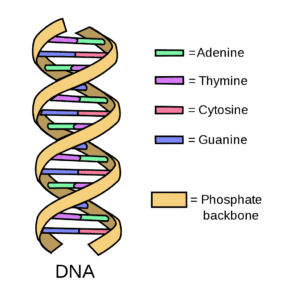
Deoxy ribonucleic Acid and RNA
DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID-
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid that carries the genetic information to the offspring of an organism. DNA forms the chemical basis...

Axial Skeleton-Vertebral Column, Thoracic cage
Vertebral Column
This consists of 24 movable bones (vertebrae) plus the sacrum and coccyx. The bodies of the bones are separated from each other by intervertebral disc...

The Skeleton-Skull
The Skeleton-
The skeleton is the bony framework of the body. It forms the cavities and fossae that protect some structures, forms the joints and gives attachment to m...
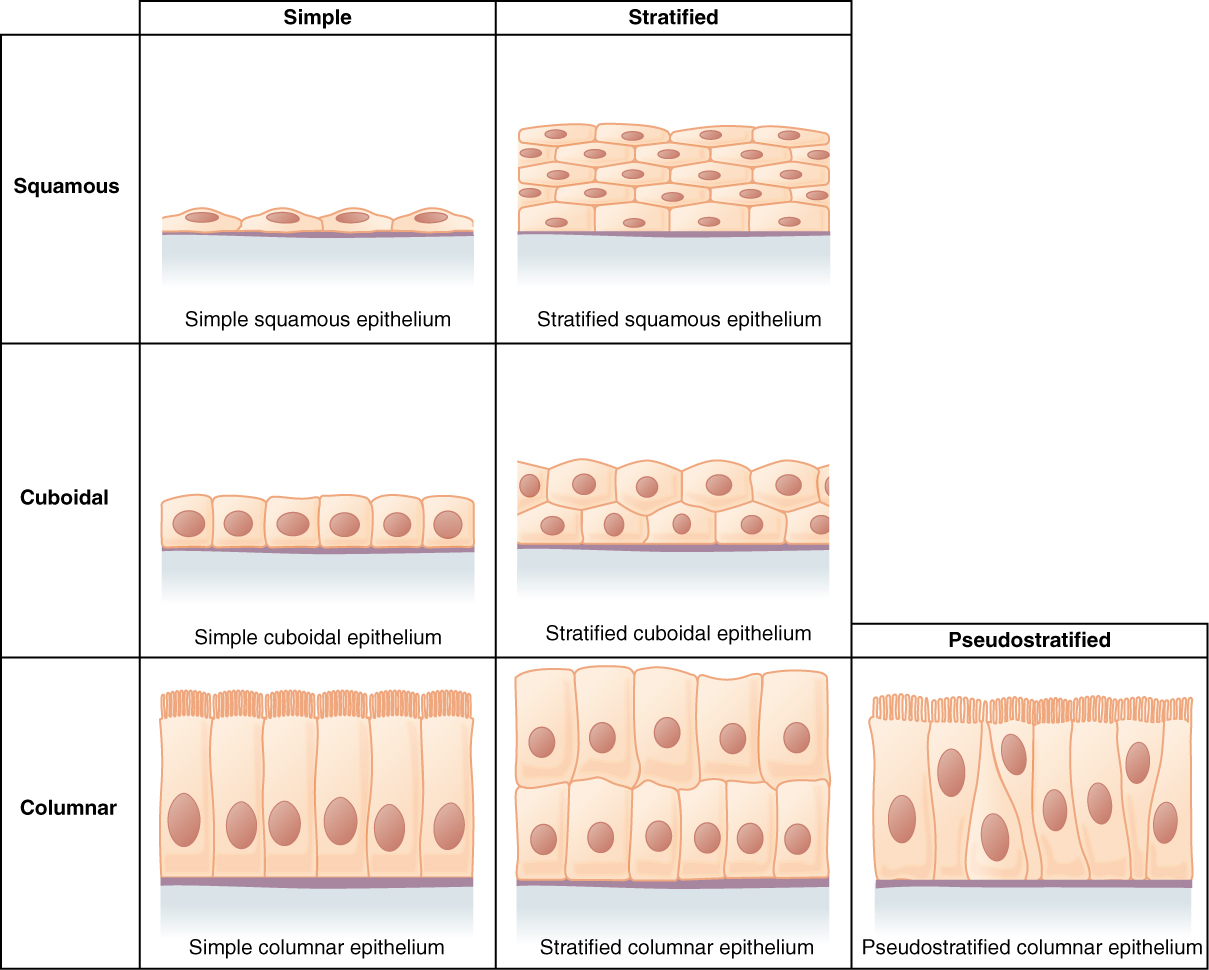
Tissue
Tissue
The tissues of the body consist of large numbers of cells and they are classified according to the size, shape and functions of these cells.
There are...
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal_cell_organelles-36b9ba0c39a44a429ccbb0702ff43d79.jpg)
Cell
Cell-
Cells are the smallest functional units of the body. They are grouped together to form tissues, each of which has a specialised function, e.g. blood, muscle, bon...