Various Position of the Patient
Position of the Patient
Various positions are provided in order to give better care and treatment for examining patients. The positions are equally important for nurses, doctors and patients as well. Before preparing a patient for operation or examination or in postoperative cases, a nurse should know how to position patient.
Definition
Human positions refer to the different physical configurations that the human body can take.
"Placing the patient in good body alignment as needed therapeutically."
PURPOSES
- To promote comfort to the patient.
- To prevent complications caused by immobility.
- To promote normal physiological functions.
- To prevent pressure sores.
- To stimulate circulation.
SUPINE/RECUMBENT POSITION
A person is in the supine position when he/she is lying straight on the back such that the front position of the body and the face are upwards. Place pillows under the upper shoulders, the neck and the head so that the head and the neck are held in the correct position. This position is used to provide comfort and for doing physical examination.
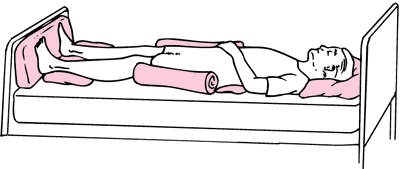
Types
- Rght lateral recumbent
- Left lateral recumbent
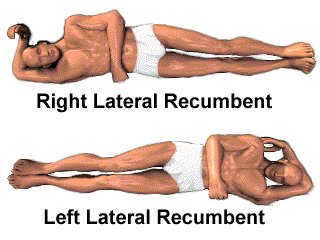
INDICATION
- Physical examinations (rectal, genital, vaginal)
- Running IV lines
- Bladder draining
- During pregnancy
- Surgical
- Drawing blood
DORSAL RECUMBENT POSITION
In this position, the patient lies flat on bed with one pillow at the head. Knee fully flexed, thigh flexed and externally rotated. Feet flat on the bed.A position in which the patient lies on the back with the lower extremities moderately flexed and rotated outward.

Indications
- Urinary catheterization
- Physical examinations (rectal, genital, vaginal)
- Surgery
- Insertion of tampons
Fowler's Position
This position is maintained by adjustable surgical bed especially of the head end. The back of patient can be kept at a comfortable inclined position by the mechanical adjustment screw. If this readymade Fowler's bed is not available, this position can be improved by placing four pillows at the back of the patient at comfortable inclination. The knees are raised over the pillow slightly to prevent slipping of patient downward.
"The Fowler's position is achieved by inclining the backrest of a bed upwards from the supine position with flexed or straight knees"
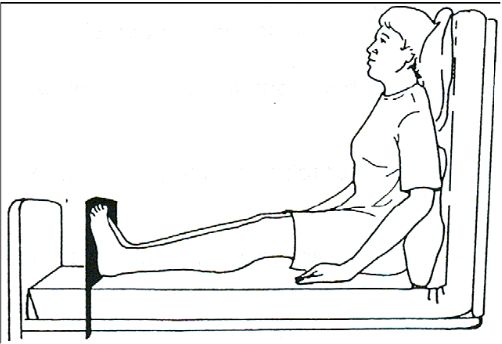
A 'low-Fowler's position is someone whose head is only slightly elevated.
- High-Fowler's position-90°
- Semi-Fowler's position-45°
- Low-Fowler's position-30°
Indications
- For relief of breathlessness.
- For facilitating drainage from abdomen and pelvic cavity postoperatively.
- To relieve or minimize dyspnea.
- To relieve tension on abdominal sutures.
- For enhanced blood circulation to prevent thrombosis.
- For good relaxation of muscles of abdomen, back and thighs.
- Helps as a comfortable half sitting position.
PRONE POSITION
This is an opposite position of recumbent position. The patient lies flat on bed with face turn to right or left side and back upwards and hands folded over pillow. One pillow is given for resting of head, chin and hands. One pillow is given under abdomen and one under legs. For women, an additional pillow is provided under the chest
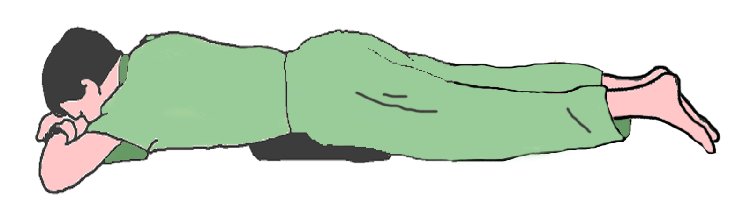
Indications
- For postoperative cases
- After tonsillectomy
- Fistula operation
- To prevent bedsore
- To relieve abdominal distension
- For postural drainage.
- Operation over spine
- Injury over the back
- Burns over the back
LATERAL POSITION
The patient lies on his left or right side with legs flexed. Patient is brought at the edge of the bed. The upper leg is flexed more than the lower leg. It is better to put one pillow for resting of upper leg behind the lower leg. The lower arm resting in the front of the patient. In this position, there is less chance of chest infection or pressure sores. Also the patient can see ward activities better in this position than in recumbent position.
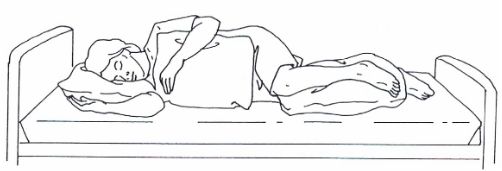
Indications
- For giving back care
- For giving enema
- For colonic irrigation
- For gynecological examination
- For rectal examination.
Avoid the following
- Lateral flexion and fatigue of sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- Internal rotation and adduction of shoulder and limited chest expansion.
- Internal rotation and adduction of femur and twisting of spine.
SIMS' POSITION
The patient lies in left lateral position slightly prone with buttocks drawn slightly backward to the edge of the bed. The right arm remains in front of the patient, whereas the left arm rests behind the patient. The right knee is well flexed against the abdomen. The left leg lies straight on the bed. For better comfort, a small pillow may be given under abdomen.
"The person lying on the left side, left hip and lower extremity straight, and right hip and knee bent. It is also called lateral recumbent position. Sims' position is also described as the person lying on the left side with both legs bent"
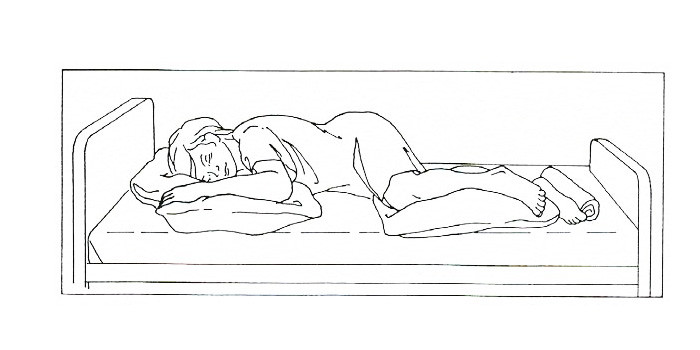
Indication
- Used for rectal examination
- Vagial examination
- For Relaxation in antenatal period.
LITHOTOMY POSITION
The lithotomy position involves the positioning of an individual's feet above or at the same level as the hip with the pelvis positioned at the edge of an examination table. Like dorsal position, the patient lies flat facing upwards. But the legs are held or fixed in position by lifting from table and hanged by stirrups or attachments especially fixed on the table.
Lithotomy position- Position in which the patient is on their back with the hips and knees flexed and the thighs apart. The position is often used for vaginal examinations and childbirth.

Indications
- For vaginal delivery and vaginal examination.
- For vaginal hysterectomy.
- Used for patients in shock.
- Used to check bleeding from lower limb.
- Used for simple pelvic examination.
- Gastrointestinal and urological examination.
- Pelvic examination.
- For rectal surgery like hemorrhoidectomy
- Child birth.
- It is used while doing operation over pelvic organs to displace intestines toward the upper abdomen.
TRENDELENBURG POSITION
In this position, the patient lies on the back with head lowered and body on inclined plane with hip higher than the head. Knees are flexed over adjustable lower section of the table which can be adjusted according to the desired height. Good padding is given over shoulder to prevent the patient from sliding towards the lower end of the table. Knees and shoulder should not be given pressure.
"Trendelenburg position, the body is lain supine, or flat on the back on a 15–30 degree incline with the feet elevated above the head."

Indication
- It is used while doing operation over pelvic organs to displace intestines to the upper abdomen.
- Management of hypotension and shock.
- Patients with deep vein thrombosis.
- Used for patients in shock.
- Bleeding from lower limb.
- Postural drainage.
KNEE-CHEST POSITION
The patient lies with chest downward facing down on the bed. Knees and thighs are flexed with buttocks high up in air The thighs remain at right angle to bed and knees take weight of hip or lower position of the abdomen. The head remains on the side with one side of cheek on pillow. The hands are flexed at elbow and rest on either side to give support to keep body on table position. A small pillow can be given under chest Abdomen remains above bed in air.

Indication
- For gynecological purposes like examination of vagina and rectum.
- For the treatment of cord prolapse and retroverted uterus.