ENEMA
Definition
- An enema is an introduction of fluid into the lower bowel through the rectum for the purpose of cleansing or to introduce medication or nourishment.
- An enema involves inserting liquid or gas into the rectum, which is the lower part of the large intestine. The aim is to empty the bowels, allow for an examination, or administer medication.
Purpose
- To stimulate defecation & to treat constipation ex: simple evacuant enema
- To soften hard faecal matter ex- oil enema
- To administer medication ex- sedative enema
- To protect and soothe the mucus membrane of intestine & to check diarrhoea ex - emollient enema
- To destroy intestinal parasites ex - anthelminitic enema
- To relieve the gaseous distention ex - carminitive enema
- To administer the fluid and nutrients ex-nutritive enema
- To relieve inflammation ex -astringent enema
- To induce peristalsis ex - purgative enema
- To stimulate a person in shock and collapse ex- stimulant enema
- To reduce the temperature ex -cold enema or ice enema
- To clean the bowels prior to x-ray studies , visualization of the bowel , surgery on the bowel or delivery of a baby ex -saline enema
- To make diagnosis ex-barium enema
- To establish regular bowel functions during a bowel training programme
- To induce anesthesia ex -anesthetic enema
Classification of enema
- Evacuant enema
- Retained enema
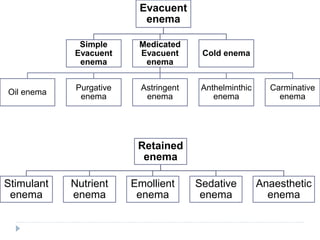
1. Evacuent enema
- Simple Evacuent enema
- Medicated Evacuent enema
- Oil enema
- Purgative enema
- Astringent enema
- Anthelminthic enema
- Carminative enema
- Cold enema
2. Retained enema
- Stimulant enema
- Nutrient enema
- Emollient enema
- Sedative enema
- Anaesthetic enema
| Evacuant Enema | Retention Enema |
| Evacuant enema are meant to be returned | Retained enemas are meant to be retained |
| A water-based formulation is used in this process | An oil-based formulation is used in this process |
| Evacuant enema has its use in increasing the water content of the stool. | The retention enema has its use in lubricating the bowel content so as to facilitate the softening of the stool |
| Evacuant Enema is used to eliminate different gaseous distension and also to increase the water content which is present in the stool. | Retention Enema is usually used in shock, collapse and some poisoning cases. |
| Evacuant enema is used in the rectum or in the lower colon. | On the hand, retention enema is usually used to lubricate the bowels |

1. Evacuent enema
A. Simple evacuant enema-A simple evacuant enema is a type of enema that uses plain warm water or normal saline to help empty the bowels, especially when someone is constipated.
Purpose
- To stimulate defecation & to treat constipation
- To relieve the gaseous distention by stimulating the peristalsis
- To relieve the retention of urine by reflex stimulation of the bladder
- To stimulate uterine contraction & to hasten the child birth
- To cleanse the bowel prior to x-ray studies , visualization of the bowels (ex: sigmoidoscopy) , surgery & retention enemas
Solutions used
- Soap & water - soap jelly 50ml to 1 liter of water
- Normal saline -sodium chloride 1 teaspoon of half liter of water
- Tap water
Amount of solutions to be used -
- Adults : 500 to 1000 ml ( 1 to 2 pint )
- Children's : 250 to 500 ml ( 0.5 to 1 pint )
- Infants : 250 ml or less
Temp of solution
- Adults : 105 to 110 degree Fahrenheit
- Children : 100 degree Fahrenheit
B. Medicated Evacuent Enema-A medicated evacuant enema is a rectally administered solution that contains both a medication and an evacuant agent, designed to stimulate bowel movements and empty the lower intestine.
a. Oil enema
- These are given to soften faecal matter in case of severe constipation
- Before the 1st bowel movement after operation on the rectum or perineum. To avoid straining & injury to the sutures & wounds
- It should be retained for half an hour to 1 hour to soften the faeces
- It should then be followed by a soap & water enema to open the bowels
Solutions used
- Olive oil
- Gingerly oil or sweet oil
- Castor oil & olive oil (1:2)
Amount of solution to be used -
- 115 to 175 ml
- Temperature of the solutions : 100 degree Fahrenheit
b. Purgative Enema
- A purgative enema is a type of medicine that helps remove unwanted waste from the body, and is also known as a laxative, cathartic, or purge.
- These are given to cause the bowel to contrast actively & to evacuate its contents
- Its acts by their irritating effect on the mucus lining, stimulate peristalsis & cause the evacuation of bowel
- The stretching of the intestine due to this inflow of fluid causes the intestine to contract & leads to the evacuation of bowels
Solutions used
- Pure glycerin – 15 to 30 ml
- Glycerin & water – 1:2
- Glycerin & caster oil – 1:1
- Magnesium sulphate : 60 to 120 ml with sufficient amount of water to dissolve it
- 1-2-3 enema : magnesium sulphate 30 ml, glycerin 60 ml, & water 90 ml
- Amount & temp of solution is that of oil enema
c. Anthelmintic enema
- This is given to destroy & expel the worms from the intestines
- Before the treatment is given the bowel should be cleansed by a soap water enema so that the drug may come in direct contact with the worms & the lining of the intestine
- The treatment is given until the worms are destroyed
Solution
- Infusion of quassia : 15gms of chips to 600 ml of water
- Hypertonic saline solution : sodium chloride 60 ml with 600 ml of water
- Amount of the solution : 250 ml
d. Carminitive enema (antispasmodic)
- These are given to relieve gaseous distention of the abdomen by causing peristalsis & expulsion of flatus &faeces
- It is given as simple evacuant enema
Solution
- Turpentine : 8 to 16 ml of turpentine mixed thoroughly with 600 to 1200 ml of soap solution
- Milk and molasses(granular sugar ) : 90 to 230 ml of molasses well mixed with equal quantity of warm milk
e. Astringent enema
- It contracts the tissues & the blood vessels , checks bleeding & inflammation , lessens the amount of mucus discharge & gives a temporary relief in the inflamed area
- It is usually given in colitis & dysentery
- They are usually given in the form of rectal or colonic irrigations
- The solution is allowed to run in slowly & return quickly to avoid distension , pain & irritation of the inflamed wall
Solutions :
- Tannic acid : 2 gms to 600ml of water
- Alum : 30 gms to 600ml of water
- Silver nitrate 2% : (silver nitrate is dissolved in distilled water)
- Temperature of the solution : It is given as hot as the client can stand
C. Cold enema (ice enema)
- This is given to decrease the body temperature in hyperpyrexia and heat stroke
- It is given in the form of colonic irrigation
Complications
- Hypothermia
- Abdominal cramps
2. Retained enema
a. Stimulant enema
- A stimulant enema is given in the treatment of shock and collapse
- It is also sometimes given in case of poisoning ex: coffee enema is given in case of opium poisoning
Solutions :
- Black coffee : 1 table spoon coffee powder to 300 ml of water
- Brandy : 15 ml of brandy added to 120 to 180 ml of glucose saline
Amount of solution
- 180 to 240 ml
- Temp of solution : 108 to 110 degree Fahrenheit
er nitrate 2% : (silver nitrate is dissolved in distilled water
b. Sedative enema
It is retention enema containing a sedative drug given to induce sleep
Drugs used
- Paraldehyde
- Chloral hydrate
- Potassium bromide
- Dose as ordered by the doctor
c. Emollient enema
This is an introduction of bland solution into the rectum for the purpose of checking diarrhoea or soothing & relieving irritation on an inflamed mucus membrane
Solution used
- Starch & opium : opium 1 to 2ml is added to 120 to 180 ml of starch mucilage or rice water
- Starch mucilage alone
- Amount of solution : 120 to 180 ml
- Temp of solution : 100 to 105 degree Fahrenheit (37.8 to 40.5 degree centigrade )
d. Anaesthetic enema
It is a retention enema containing an anesthetic drug to produce anesthesia in client
Drugs used :
Avertin 150 to 300 mg per kg of body weight.
e. Nutrient enema
- It is a retention enema to supply food & fluids to the body
- Selection of the fluids depend upon the ability of the colon to absorb it
- Nutrient enema is particularly useful in conditions like haemophilia which makes I.V. infusion difficult or undesirable
Solutions :
- Normal saline
- Glucose 2 to 5%
- Peptonized milk 120 ml
Amount of solution
1100 to 1700 ml in 24 hour or 180 to 270 ml at 4 hourly interval
Temperature of solution
100 degree Fahrenheit (37.8 degree Fahrenheit )
General instructions
- The appropriate size catheter or rectal tube need to be used
- The rectal tube needs to be smooth and flexible
- The rectal tube is lubricated with water soluble lubricant
- The temperature of the solutions needs to be adjusted according to the purpose of enema
- The amount of the solution to be administered depends upon the type of the enema and the age & size of the person
- When enema is administered, the client usually assumes a left lateral position
- The distance to which the tube is inserted depends upon the age and the size of the client
- The height of the can should be adjusted to regulate the flow of the solution according to the type of the enema
- The length of time that the enema solution is retained will depend upon the purpose of enema and the ability of the client to contract the external sphincter to retain the solution
- Make sure the whole apparatus used for the administration of enemas is in a good working condition
- Regulate the flow of fluid according to the type of the enema, give retention enema very slowly, usually by a Murphy drip.
- If the rectum is impacted, attempt to remove the faecal matter with gloved finger.
- Listen to the complaints of the client and should not ignore
Note-The placing or hanging your enema bucket or enema bag no more than 18 inches above your buttocks.
Articles
- Disposable gloves
- Water soluble lubricant
- Bath thermometer
- Soap and water
- Toilet tissues
- Enema can
- Tubing and clamp
- Appropriate size rectal tube
- Adult : 22-30 Fr
- Child size : 12-18 Fr
- IV stand
- K . Basin(2)
- Solution as ordered
- Mackintosh/waterproof under pad
- Bedpan
Procedure
- Assess status of patient
- Last bowel movement
- Normal bowel pattern
- Mobility
- Abdominal pain etc.
- Determine the level of consciousness and understanding, provide privacy
- Explain procedure purpose to the patient
- Assemble articles, wash hands and don gloves
- Raise the bed to appropriate height
- Assist patient to side lying position (sim’s position)
- Place mackintosh under hip and buttocks
- Cover the patient exposing only anal area, clearly visualizing anus
- Place bed pan or commode in easily accessible position
- Check temperature of solution on inner wrist
- Raise container, release clamp and allow solution to flow long enough to fill tubing
- Clamp the tubing lubricate 6-8 cm of tip of rectal tube with jelly Separate the buttocks and locate the anus. Instruct patient to relax by breathing out slowly through mouth
- Insert –tip of rectal tube gently by pointing the tip in the direction of patients umbilicus
- Adult : 7.5-10 cm(3-4 Inch)
- Child : 5-7.5 cm (2-3 Inch)
- Infant : 2.5-3.7 cm (1-1.5 Inch)
- Hold the tubing in place with one non- dominant hand.
- Open regulatory clamp and allow solution to enter slowly with the container at the patients hip level.
- Raise the enema can slowly to appropriate level above the anus. Eg: for the infusion rate 1L in 10 mt.
- Lower container or clamp tubing for 30seconds.If patient complaints of cramping or if fluid escapes around rectal tube.
- Clamp tubing after all solution is instilled.
- Inform patient, that fluid instillation is over and the tube will be removed.
- Place layers of toilet tissue around tube at anus and gently withdraw rectal tube.
- Explain to patient that feeling of distention is normal and ask patient to retain solution as long as possible (5-10 mts)while lying quietly in bed.
- Discard the disposable, used items in proper receptacle. If enema can needs to be reused. Rinse out thoroughly with soap and warm water.
- Assist patient to toilet or help to position on bed pan.
- Observe the fecal matter and expelled solution.
- Assist as needed to wash anal area with soap and water.
- Remove and discard gloves and wash hands.
- Assess condition of patient abdomen may indicate serious problems.
- Record type and volume of enema given and characteristics of return flow.
- Report failure to defecate to the physician
- Clean and replace the reusable articles. Discard any waste and disposable items.