Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary Artery Disease-
Pathological condition of coronary Artery in which Narrowing and obstruction partially or completely due to excessive accumulation of fat and cholesterol result lesion/Atheroma. decrease supply in heart. Due to decrease supply in myocardium ischemia, narcosis congestive cardiac arrhythmia, hypertension and structural damage may occur.
Condition of coronary Artery get narrower and reduce the blood flow to the heart. It is the usual underlying cause of a heart attack. Coronary heart disease is associated with age and is a lifelong condition that affects many people.
Cause of Obstruction-
- Atheroscluosis
- Arterioscluosis
- Artiritis
- Coronary thrombosis
- Embolism
Risk fctors associated with Incidence of CAD-
- Age-Atheroscluosis development start as early as 15 years of age continue as age progresses.
- Sex- men have a great risk.after menopause Women has equal risk.
- Race-Caucasians are more prone.
- Family history and heredity
Modifiable Risk factors-
- Hypelipidemia
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Physical inactivity
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Stress
- Oral contraceptives
Clinical Manifestation-
Clinical manifestation depend on-
- Size of obstruction
- No of obstruction
- Which Artery effected
- No of Artery Effected
- Fatigueless
- Weakness
- Activity intolerance
- Chest pain
- Sudden increase heart rate
- Coughing
- Tachycardia
- Hypertension
- Shortness of breath
- Tachypnea
- Sweating
- Convulsion
- Palpable Heart sound
Diagnostic Investigation-
- History collection
- Physical examination-increase blood pressure, slight tachycardia
- ECG-no changes
- TMT (Trade mil test)- TMT test is also called Exercise Stress Test, Computerized Stress Test or simply Stress test.
- Stress test
- Cardiac catheterization
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Electron beam (ultrafast) CT scan
- Exercise stress tests
- Coronary Angiography-Inject dyes to find out blockage.
- Lipid Profile- Increase LDL, increase cholesterol, decrease HDL, Increase Homocysteine
- LFT- Liver function tests are used to measure specific enzymes and proteins in your blood.
- RFT- Kidney Function Test
Management-
Modification-
Pharmacological management-
1. Nitrate and nitrate preparation- Function-Vasodilator, increase perfusion, Decrease Demand
- Sorbitol
- NTG (Nitroglycerin)
- Isosorbide Mononitrate
- Isodiol
2. B-Adrenergic Blocker- Beta-adrenergic blocking agents are used to treat angina, control abnormal heart rhythms and to reduce high blood pressure.(Function Decrease adrenergic/Sympathetic stimulation. Decrease Heart Rate, palpitation, Decrease O2 Demand)
eg- Propranolol, Mataprolol, Timolol, Atenol
Note- The names of all Beta-blockers end in "-olol" except for labetalol and carvedilol.
3. Calcium channel Blocker.-Decrease Contraction, Decrease stroke volume. Decrease BP, Decrease O2 Demand, Vesodilation of Blood Vesscle,
Eg-
- Amlodipine (Norvasc)
- Diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac, others)
- Felodipine
- Isradipine
- Nicardipine
- Nifedipine (Adalat CC, Procardia)
- Nisoldipine (Sular)
- Verapamil (Calan, Verelan)
4. Antilipidemic- Antilipemic drugs Drugs used to lower lipid levels Used as an adjunct to diet therapy-Drug choice based on the specific lipid profile of the patient.
Surgical management-
Percutaneous trans luminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)- It is diagnostic and therapeutic procedure .in which a catheter insert through the lumen. Route by which catheter Insert-
- Femoral Artery
- Brachial Artery
- Radial Artery
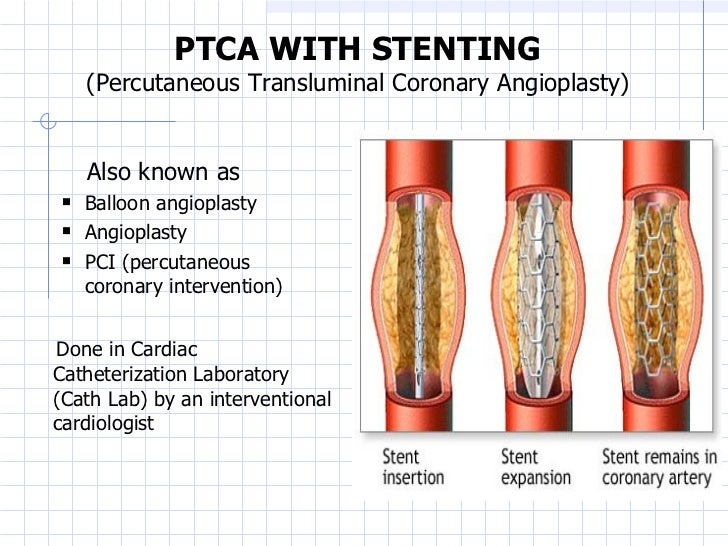
1. Ballon Angioplasty- Balloon angioplasty is a medical procedure that is performed to open up arteries that have been narrowed by plaque. Balloon angioplasty is a safe and commonly performed procedure, and is now considered standard PAD treatment.
2. Atherectomy-removing of Atheroma./plugue and cutting chamber use and rotating blade.
3. Stent -coronary Artery Stent
Coronary Artery bypass Grafting (CABG)- A coronary artery bypass graft (CABG or CAG) is placed during a surgical procedure to increase blood flow to the myocardium due to coronary stenosis, usually caused by coronary artery disease. Arteries or veins can be grafted during this procedure. Long term outcome of coronary artery bypass grafting depends on graft patency.
Cardio pulmonary bypass- Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which a machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery, maintaining the circulation of blood and the oxygen content of the patient's body.