Disease Producing RNA Viruses
Disease Producing RNA Viruses-
An RNA virus is a virus that has RNA (ribonucleic acid) as its genetic material. Another term for RNA viruses that explicitly excludes retroviruses is ribovirus.
- Poliomyelitis Viruses
- Rhino Viruses
- Orthomyxo Viruses (Influenza Viruses)
- Paramyxo Viruses
- Mumps Virus (Rabula inflans)
- Measles Virus (Rubeola or Morbilli)
- Parainfluenza Viruses
- Rhabdo Viruses (Rabies Viruses)
- German Measle Viruses (Rubella Viruses)
- Arbo Viruses (Arthropod Borne Viruses)
a. Mosquito Borne Arbo Viruses
- Chikungunya Viruses
- JBE Viruses (Japanese B Encephalitis Viruses)
- Yellow Fever Viruses
- Dengue Fever Viruses
b. Tick Borne Arboviruses- KFD Viruses (Kyasanur Forest Disease Viruses)
- Corona Viruses
- Rota Viruses
- Retro Viruses (Oncogenic or Tumour Producing RNA Viruses)
- HTLV (Human T cell Leukemia Viruses HTLV-1 and HTLV-2)
- HIV (Human Immuno Deficiency Virus HIV-1 and HIV-2)
Poliomyelitis Viruses-
These are smallest spherical viruses present in the cytoplasm of infected cells and cause poliomyelitis (Infantile paralysis) disease. There are three distinct types of poliomyelitis viruses (Type I, II and III) and each type includes a number of strains. Type I is the commonest and responsible for the epidemic. These viruses can survive in faces for several weeks. Faeces of patient and carrier is the important source of polio virus. The disease spreads through contaminated drinking water, sewage etc.
- Cause- poliovirus spread by fecal-oral route
- Symptom -Muscle weakness
- Prevention –Polio vaccine
- Incubation period is about ten days with range from 4 days to 4 weeks.

Its principal portal of entry is the gastrointestinal tract via mouth. These viruses multiply in the mucous membrane of the pharynx and intestine and then spread to the blood and finally reach the nervous system. They cause inflammation of the spinal cord, damage motor cells and the motor responses to the affected parts are weakened or destroyed.
The incubation period is about ten days with range from 4 days to 4 weeks. Two types of vaccines viz. Sabin’s live polio vaccines and Salk’s killed polio vaccines are available. Salk’s vaccine is given by injection and Sabin’s vaccine is given orally. Sabin’s vaccine is economical and single oral dose gives lifelong immunity. Salk’s vaccine is given by injection in 2 or 3 doses and it is followed by booster doses.
Rhinoviruses-
Rhino means nose Infection cause the common cold. They are so named because of their special adaptation to grow in the nose. There are at least more than 100 serotypes of Rhinoviruses. Because of so many serotypes, it has not been possible to make ideal efficient composite vaccine. They are responsible for the common cold.
The disease is trasmitted by droplets. The incubation period is 2 days. Human is the only natural host of rhinovirus.
Orthomyxoviruses (Influenza Viruses)-
They are mostly spherical viruses and multiply in nucleus as well as in cytoplasm. They are enveloped with spikes on its surface. Influenza viruses are of three main types, A, B and C. There are many strains in type A and B and new strains are still appearing in both these strains.
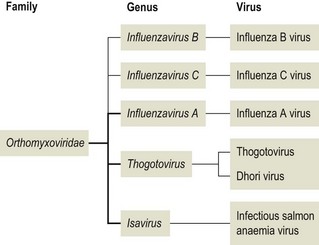
Type A and B cause epidemic influenza but type C causes very mild disease. Influenza is an acute infectious disease of the respiratory tract of man, the incubation period being 1-3 days.
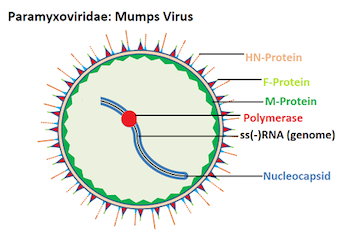
Paramyxo Viruses
Is a family of negative- sense, single-stranded RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales.
They resemble orthomyxo viruses in morphology but are much larger in size. This virus multiplies in cytoplasm and is enveloped with spikes on its surface .These include mumps viruses, measles viruses and par influenza viruses etc.
1. Mumps Virus (Rabula Inflans)-It causes mumps disease and humans are the only natural hosts. The incubation period is 21 days. Infection may be by inhalation or through the conjunctiva. Since mumps virus causes acute inflammation of the parotid glands, the disease is also called epidemic paratitis. To begin with, the parotid glands show inflammation with marked swelling behind the ear and there is difficulty in swallowing. Mumps virus may produce complications in brain, meninges, thyroid, pancreas, breast, ovaries, testes and the heart. Inflammation of the testis is common in adult males which may sometimes even lead to sterility.
2. Measles Virus (Rubeola or Morbilli) -It causes measles, one of the most common infectious world -wide viral diseases of children. The incubation period is 10 to 12 days. After 10 days the patients begin with fever, cough and respiratory infection in the upper tract. Spots called kaplik’s spots appear on the buccal mucosa. The disease is sometimes complicated by secondary bacterial infection such as pneumonia, bronchitis and very rarely severe infection encephalitis can also occur.

3. Parainfluenza Viruses -They are classified into 4 types: parainfluenza types 1-4. Type 3 causes lower respiratory tract infections (bronchitis, bronchiolitis) while type 4 causes minor respiratory infection. Type 1 and 2 cause severe infections.

Rhabdo Viruses-
The term rabies is derived from the Latin word “Rabidus” meaning “Mad”. These viruses are bullet shaped and multiply in neuroplasm but at times these also multiply in salivary glands. It is surrounded by lipoprotien envelope from which project spikes. In infected brain the characteristics cell inclusions known as negri bodies are present in the nucleoplasm. Rhabdo virus causes the disease rabies also called hydrophobia because the patient shows fear of water and is unable to drink in spite of being very thirsty.
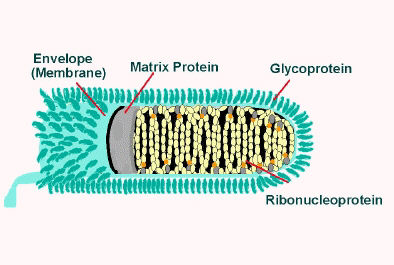
The incubation period varies from 1 to 3 months though it may be as short as 10 days or as long as 3 years. The incubation period depends upon the site of the wound and its distance from the brain. If the site of the wound is near the brain the incubation period will be fairly short. The disease is transmitted chiefly through the saliva of rabies dog. Humans are infected by the bite of a rabid dog or any other rabid mammal and the virus spreads from the wound through the nerve fibre to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). From central nervous system virus spreads to salivary glands and other tissues.
The disease is characterized by depression, itching at the site of primary infection, fever, paralysis of the face muscles, eyes and tongue and then spreads to the limbs. Fear of water is the dominant symptom which leads to convulsions, coma and death.
Rubella Virus (German Measle Virus)-
Rubella virus causes German measles. It is surrounded by an envelope with spikes, on its surface. It is not as highly infective as measles but it has a tendency to develop complications. The virus is inhaled and grows in mouth and throat and small white patches are seen in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. After the incubation period (16 to 18 days), the patient develops fever and skin shows blood rashes.
- Symptom- Rash, swollen lymph nodes fever
- Cause- Rubella virus (spread through the air)
- Complication-Testicular swelling (Orchitis)
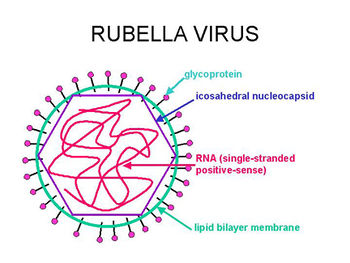
The virus may also spread up to middle ear and attack lymph glands. Arthritis is common complication especially in females. The infection may be transmitted by the pregnant mother to the foetus and the foetal cells may be damaged. The foetus may die or develop some serious heart abnormalities, large liver, large spleen, etc. It is transmitted by nasopharyngeal secretions borne in the air or dust.
Arboviruses (Arthropod Borne Viruses)-
‘Arbo virus’ is a short form of ‘arthropod borne virus’. It is enveloped spherical virus and multiplies in arthropods (mosquito and tick). Arbo Viruses may be mosquito borne (Chikun gunya viruses, JBE viruses, Yellow Fever viruses, Dengue Fever Viruses) or tick borne (RSSE viruses, KFD viruses).
a. Mosquito Borne Arbo Viruses
1. Chikungunya Viruses- They cause chikungunya disease in man and are transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquito. It occurred in Africa in 1952, Thailand in 1958 and in India in 1963. In India it caused very extensive epidemic in Kolkata, Tamil Nadu and other areas. In 1975, it occurred as an endemic in Maharashtra. The disease is characterised by fever, joint pains, conjunctivitis and lymphadenopathy.
2. JBE Viruses (Japanese B. Encephalitis Viruses)- This disease is transmitted through Culex mosquito. It occurred in Korea, Japan, India and Malasia. In 1935 it occurred in Japan as a very severe epidemic. It was recognized in India in 1955 and epidemics have been reported in West Bengal, Bihar and Assam in 1973 and latest in 1978. The disease is characterised by chill, fever, headache, nausea, vomiting and pain. The patient feels drowsy and in several cases it may result in mental confusion, coma and death. The incubation period is between 4 to 21 days.
3. Yellow Fever Viruses- Yellow fever virus is the first human virus which was discovered in 1900 by Walter Reed. It causes yellow fever in man but it does not occur in India. It is spread by Aedes aegypti mosquito and the incubation period is 3 to 6 days. The disease starts with high fever, chills, headache, nausea, vomiting and backache and does great damage to the liver, kidney and blood vessels causing jaundice, albuminuria, and hemorrhage’s in the gastro-intestinal tract and the patient may die of hepatic and renal failure.
4.Dengue Fever Viruses-
- Species -Dengue Virus
- Genus- Flavivirus
- Family- Flaviviridae
These are transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquito from man to man and cause Dengue Fever in India. There are four strains of this virus: Den-1-4. All the four strains are identified in India but it is Den 2 and Den 3 virus which claimed the lives of hundreds of people in Delhi in 1996-97. Dengue Fever is also called as break bone fever because there is severe backache.
The symptoms are very high fever, low platelets count, vomiting with blood and black colored stool, headache, joint pains, stiffness etc. When a person suffers from dengue and it reaches the hemorrhagic stage, the functioning of the bone marrow, where all the blood components are made, gets affected. Fresh blood stops flowing in the arteries and the existing platelets are consumed. There is a sudden fall in the platelets count resulting in internal bleeding. Timely fluid therapy and platelets transfusion only can save a patient.
b. Tick Borne Arbo Viruses Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD) Viruses-
These viruses are tick borne and cause Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), first noticed in Kyasanur forest area in Karnataka State in India. They are carried from human to human by ticks and the patient develops haemorrhages in skin, mucosa and viscera. This disease is also called haemorrhagic fever.
Corona Viruses-
They are enveloped viruses with widely spread club shapes projections on its surface. Corona virus has many serotypes and it is responsible for common cold and acute respiratory infections.
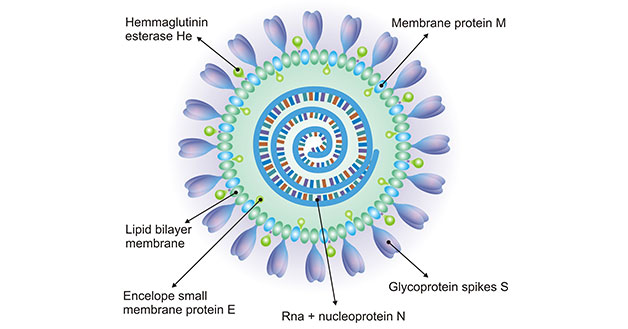
Rota Viruses The name is derived from rota meaning wheel. These viruses are characterized by well-defined outline like rim of wheel and on its outer rim short projections are present. Rota viruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal diseases in infants and children. The incubation period is 2 to 3 days.
Retro Viruses-

Two types of retro viruses’ viz., Human Tcell Leukemia Virus (HTLV) and human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) are responsible for causing human diseases. At present there are two strains of HTLV, viz. HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 which have been isolated and both are basically similar. They are enveloped viruses that develop by budding through the host cell membrane and cause leukemia disease, a type of blood cancer formed by the excessive growth of leucocytes. They are usually transmitted from mother to the child. HIV also has two strains HIV-1 and HIV-2 giving rise to slowly developing disease AIDS. We will discuss this disease separately under the title HIV and AIDS.