Abortion
Abortion
Expulsion from the uterus of an embryo or fetus prior to the stage of viability, which is 20 weeks gestation, or fetal weight less than 500gm.
Abortion, the expulsion of a fetus from the uterus before it has reached the stage of viability (in human beings, usually about the 20th week of gestation).
Classification /Clinical types
A. Spontaneous
- Inevitable
- Complete
- Incomplete- Septic
2. Threatened
- Pregnancy continuous-Viable baby takes birth
- Missed abortion- blood mole- Corneous mole
B. Induced-
- Criminal- Septic
- Therapeutic
C. Recurrent Abortion
Etiology
- Oro-foetal causes
- Maternal environment
1. Oro-foetal causes will operate in early pregnancy including-
- Chromosomal abnormality like autosomal trisomy and gross congenital malformations.
- Low attachment of the placenta and faulty placental formation.
2. Maternal environment will operate in mid pregnancy abortion.
- Viral infection specially rubella, cytomegalic
- Chronic illness e.g., Hypertension and chronic Nephritis and endocrine factors like hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus
- Inadequate corpus luteal phase
- Cervical incompetence
- Congenital malformations of the uterus like bicornuate or septate uterus
- Uterine fibroids
- Deficiency of folic acid and Vitamin E
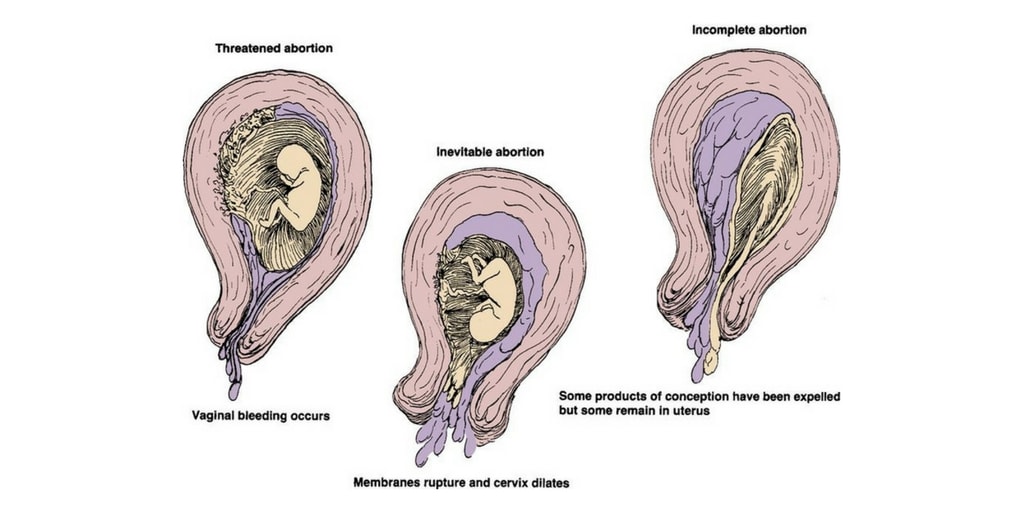
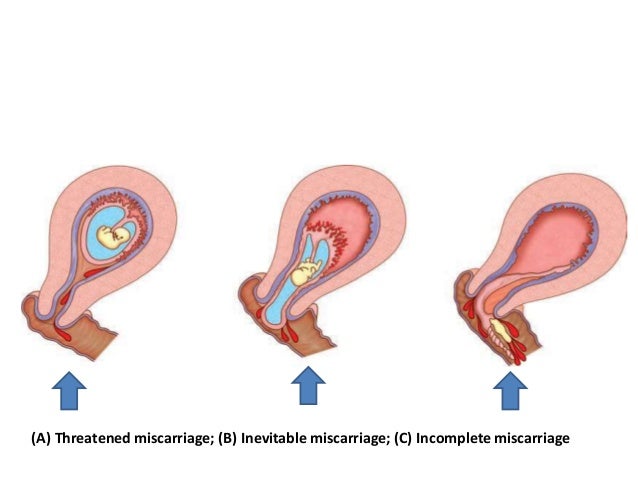
Threatened Abortion-
A clinical entity where the choriodecidual haemorrhage (the process of abortion) has begun, but not progressed to the stage of irreversibility. The cervix is not open and the product of conception are not expelled.
Slight vaginal bleeding occurs in early pregnancy associated with closed cervix. The pregnancy may continue or result in an abortion.
Clinical Manifestations
- Symptoms suggestive of pregnancy
- Vaginal bleeding is scanty and bright red in colour
- Lower abdominal discomforts and pain. Mild uterine cramps and back pain
- No history of expulsion of clots or fleshy lumps
- Bimanual examinations elicit cervical Os as closed and blood-stained discharge.
- Uterus soft
Investigation
- Haemoglobin estimation
- Urine pregnancy test
- Serum HCG
Nursing Intervention
- Bed rest for 5-7 days, proper sleep and avoid stress and excitement.
- Assess amount of blood loss.
- Investigations of blood urea and ultrasonography are routinely done.
- Report immediately if bleeding or pain increases.
- Routine monitoring of vital signs.
- Advice on discharge will include bed rest for two weeks, avoidance of heavy and strenuous exercises and report after a month for examination.
- Prognosis is unpredictable. In about two-third of cases the pregnancy continues beyond 28 weeks, in the rest it terminates in inevitable abortion or missed abortion.
Inevitable Abortion-
In this type abortion, the process of abortion has begun and progressed to such an extent that expulsion of the product of conception seems inevitable.
It involves a moderate to heavy amount of uterine bleeding with an open cervical os. In complete abortion the conceptus is expelled completely from the uterus while in incomplete abortion the entire products of conception are not expelled.
Clinical Manifestations
- History of amenorrhoea for some weeks or months.
- Vaginal bleeding is heavy with clots or conceptus.
- Severe colicky lower abdominal pain
- Cold, clammy extremities.
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Shock
- Internal examination shows dilated os through which the conceptus is felt and membranes may be ruptured.
Investigation-
- Blood group and cross matching
- Haemoglobin
- EWBC total and differential
- Ultrasonography
Obstetric Management and Nursing Interventions
- Advised for hospitalization and bed rest
- Prompt termination of pregnancy usually by dilatation and curettage is required. Preparation of the mother physically and psychologically.
- Intravenous fluid therapy and blood transfusion.
- Psychological support
- Prevention of infection.
- Tetanus toxoid and anti -D for RH – negative mother
Complete Abortion
In complete abortion the product of conception is expelled completely (en mass) from the uterus and the uterine cavity is empty.
Clinical Manifestations
- History of short amenorrhoea and expulsion of fleshy mass per vaginum followed by cessation of abdominal pain.
- Vaginal bleeding becomes less.
- Signs of pregnancy regress
- Lower abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding with passage of fleshy mass
- Decrease in bleeding and pain following expulsion of product of conception
- On palpation the uterus is firmly contracted and the empty cavity is seen on ultrasonography.
Obstetric Management and Nursing Interventions
- If doubt about complete expulsion of the conceptus, the uterine curettage is usually done. For this preparation of the woman and assisting the doctor.
- Inj. Tetanus vaccine and Anti-D gamma globulin is usually prescribed.
- Psychological support.
- Sedatives
- Haematinics if blood loss was significant
Incomplete Abortion
The entire product of conception is not expelled and a part of it is left inside the uterine cavity.
Clinical Manifestations
- Heavy vaginal bleeding and history of expulsion of fleshy moles.
- Uterine cramping is severe
- The cervical canal is dilated
- Lower abdominal pain of colicky nature.
- Internal examination will reveal the uterus smaller than the period of amenorrhoea.
Investigation
- Blood group and cross matching
- Haemoglobin
- WBC
- Ultrasonography
Obstetric Management and Dilatation Nursing Interventions
- To combat shock resuscitative measures are undertaken
- Dilatation and curettage are usually done
- The removed material is sent for histopathological examination
- Psychological support
- Prevention of infection.
Missed Abortion
In missed Abortion the fetus is dead and retained inside the uterus for a variable period of time.
The foetus dies and is retained within uterus for four weeks or more.
Pathophysiology
Dead products of conception are converted to avoid tough fleshy mass due to recurrent or slow and progressive haemorrhage is choriolodecidual space. This is known as blood mole or fleshy mole. The embryo shrinks and degenerative changes like maceration and mummification occur.
Clinical Manifestations
- History of amenorrhoea and features of threatened abortion
- Persistent brownish vaginal discharge
- Cessation of symptoms of pregnancy
- Foetal heart sound not audible
- Uterine size smaller than the period of amenorrhea.
- Retrogression of breast change
- Vaginal examination shows cervical os closed and tarry vaginal discharge
- Diagnosis can be confirmed by ultrasonography
Investigation
- Pregnancy test become negative
- Ultrasonography
- Doppler examination reveals absence of FSH
- Immunological test for pregnancy – negative
- Serum fibrin degradation products (FDP) bleeding and clotting times, and platelet count if DIC is suspected.
Obstetric Management and Nursing Interventions
- Pregnancy is terminated by method appropriate to the duration of pregnancy, necessary preparation and assistance is done.
- If the uterus is less than 12 weeks size, dilatation and evacuation to empty the uterine cavity is done. The labour is induced if the size of the uterus is more than 12 weeks.
- If the foetus is retained for more than 5 weeks and pregnancy is more than 12 weeks, disseminated intravascular coagulation and in coagulability of blood resulting into uncontrolled haemorrhage may develop. So, blood clotting factors are monitored.
- Uterus more than 12 weeks- Ripening of the cervix with prostaglandin gel and then 2 hourly injections of prostasin.
Septic Abortion
A type of abortion associated with sepsis of the products of conception. there is increase association of sepsis in illegal induced abortion because of-
- Improper antiseptic and aseptic measures
- Incompletes abortion
- Inadvertent injury to the genital organs and adjacent organs.
Infection of products of conception and uterus frequently seen as a complication of induced or incomplete abortion.
The infection is ascending, the incidence is about 10% of all abortions and is polymicrobial.
Pathophysiology
There are colonies of bacteria seen in the necrotic conceptus beginning as endometritis and thus becoming peritonitis and septicaemia.
Clinical Manifestations
- History of amenorrhoea with vaginal bleeding followed by foul purulent vaginal discharge along with pain in lower abdomen.
- High temperature & tachycardia. Subnormal temperature is ominous feature of endotoxic shock.
Nursing Interventions
- Investigations like high cervical swab, blood culture, ABO Blood grouping and Rh typing is done.
- Physical psychological care as it is rendered for a critically ill patient.
- Observe aseptic precautions during vaginal examination and related operations.
- Assisting in complete evacuation of uterine cavity in case of invitable abortion.
- Family planning measures to be encouraged to curb unwanted pregnancy.
- The mother is kept in isolation; sepsis is controlled by antibiotics–oral or intravenous.
- Intravenous infusion initiated and monitored.
- Vital signs, urinary output and progress of pain are noted.
Recurrent Abortion/Habitual Abortion
Spontaneous abortion occurring consecutively for three or more occasions. Two-third occurring beyond 12 weeks and rest in early pregnancy. It is caused by lack of immunoglobulin G, hormonal deficiency and a very important cause—cervical incompetence.
Aetiology-
- Systemic maternal disorder such as syphilis. Diabetes mellitus, chronic nephritis essential hypertension and Rh incompatibility
- Cervical incompetence
- Developmental abnormalities of uterus such as bicornuate uterus and septic uterus
- Chromosomal defects in the fetus
- Idiopathic causes.
Clinical Manifestations
- History of repeated abortions commonly occurring at 16-20 weeks without apparent cause.
- On internal examination the cervix is dilated.
Management and Nursing Interventions
- During non-pregnant state complete history is recorded, general health and pelvic examination for cervical incompetence is done. Laboratory tests like blood, urine cervical culture, hysteroscopy, ultrasonography and D & C for uterine cavity abnormality is done.
- During post conception if any infection, it is to be treated.
- Proper prenatal care emphasizing on health promotion.
- Cerclage operation for cervical incompetence is usually done. The Shirodkar or McDonald operations are undertaken. The stitches are removed at 38th week or earlier.
- The mother is instructed to report immediately if there is bleeding. Advised for regular antenatal check-ups and hospital delivery.