QUALITY ASSURANCE IN NURSING
QUALITY ASSURANCE IN NURSING
INTRODUCTION-
The expense of quality is an interactive process between customer & provider. quality assurance usually focuses on material, good work & service provided effectively. any lack in service provided causes decrease in quality.
QUALITY
It is degree to which health services for individuals & population increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes & are consistent with current professional knowledge.
-Joint Commission on Accreditation of health care organization ,2002 (JCAHO)
ASSURANCE-
It is statement or indication that inspires confidence.
QUALITY ASSURANCE –
Quality assurance is an on-going, systematic, comprehensive evaluation of health care services & impact of those services on health care services. -Kozier
• Quality assurance is defined as all activities undertaken to predate & prevent poor quality.
-Neetvert
OBJECTIVES
- To ensure the delivery of quality client care.
- To demonstrate efforts of health care providers to provide good results.
- To formulate plan of care.
- To evaluate achievement of nursing care.
- To support delivery of nursing care with administrative & managerial services.
- To explain quality assurance models as pre- requisite for quality nursing care.
- To state code of ethics & professional conduct for nurses in India.
- To appreciate importance of practicing standard safety measures.
- Plan & conduct patient teaching sessions.
- To identify appropriate management techniques to be used for managing resources in given situation.
PURPOSES
- It is required to introduce code of ethics & professional conduct for nurses in India.
- To prepare staff nurse for implementation quality assurance model in nursing.
- To provide best care to patients by maintaining standards.
PRINCIPLES
1. Customer focus- It focuses on patient’s care with standard & recent medical knowledge.
2. Leadership – It helps to inculcate qualities of leadership in staff.
3. Involvement of People- It should involve maximum nursing staff so that standards can be maintained.
4. Process approach- There should be a systematic & planned approach to provide quality care.
5. Factual approach to decision making- There should be fact or appropriate reason in taking certain decision for quality assurance of patient.
APPROACHES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE PROGRAM
Approaches of quality assurance are divided into 2 types:
- General Approach
- Specific Approach
GENERAL APPROACHES
It involves large governing of official body’s evaluation of person’s or agency’s ability to meet standard at a given time.
1. CREDENTIALING - It is process of determining & maintaining nursing standards.
Functional Components Of Credentialing Process
According to Hinsvark, credentialing process has 4 functional components:-
- To produce a quality product.
- To confer a unique identity.
- To protect provider & public.
- To control the profession
2. LICENSURE- Individual licensure is a contract between profession & state in which profession is granted control over entry into & exists from profession & over quality of professional practice.
3. ACCREDITATION- Accreditation is the act of granting credit or recognition especially to an educational institution that maintains suitable standards.
4. CERTIFICATION- Certification is usually a voluntary process within the professions. A person’s educational achievement, experience & performance on examination are used to determine person’s qualification for functioning in an identified specialty area.
2. SPECIFIC APPROACHES
Quality assurances are methods used to evaluate identified instances of provider and client interaction
1. Peer review committee- These are designed to monitor client specific aspects of care appropriate for certain levels of care. The audit is used by peer review committee to ascertain quality of care.
2. NURSING AUDIT – Nursing audit is evaluation of patient care through analysis of written records maintained by nurses in patient’s treatment profile.
- Avtar Brar
GOALS OF NURSING AUDIT
- To improve quality of health care.
- To promote improved communication among nurses & other health team members.
- To improve quality of nursing care.
- To detect & analyze problems & errors.
ADVANTAGES OF NURSING AUDIT
- Provides quality of nursing
- A patient is assured of good services.
- It will give valuable and pertinent information for the staff.
- It will lead to between co-operation and communication among the nurse & health team.
- It will help each professional nurse for her self evaluation.
- It helps the administration as better planning.
- It will reduce the incidence of medical legal complication.
- It will broaden and strengthen nursing service.
3. Utilization Review
Utilization review activities are directed towards assuring that care actually needed and that the cost appropriate for the levels of care provided
TYPES OF UTILIZATION REVIEW
- Prospective: It is an assessment of the necessary of care before giving services.
- Concurrent: A review of the necessity of care while the care is being given.
- Retrospective: It is analysis of the necessity of the services received by the client after the care has being given
4. Evaluation Studies
Donabedian’s Structure-Process-Outcome model Donabedian introduced 3 major method of evaluating quality care:-
1. Structural evaluation- This method evaluates setting & instruments used to provide care such as facilities, equipments & characteristics of administrative organization & qualification of health provider. The data can be obtained from existing documents.
2. Process Evaluation -This method evaluates activities as they relate to standards & expectations of health providers in management of client care. Data is collected through direct observations, review of records, audit etc.
3.Outcome Evaluation- The net changes that occur as a result of health care or net results of health care. The data of this method can be collected from vital statistics records such as death certificate or telephone client interview, mailed questionnaire & client records.
MODELS OF QUALITY ASSURANCE
System Model System model is used for implementation of unit based quality assurance program. It involves making changes in organizational structure & individual roles. In system model, task is broken down into manageable components based on defined objectives.
Basic Components of System Models
- Input- The input can be compared to the present state of systems. • Throughput- It is developmental process.
- Output- It is finished product or result.
- Feedback- It is essential component of system because it maintains & nourishes growth.
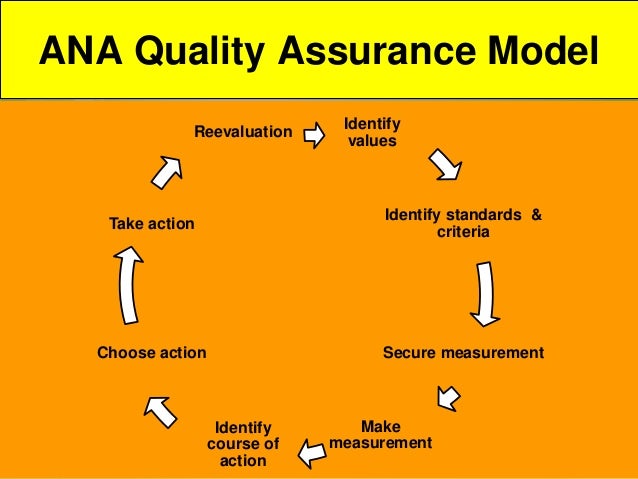
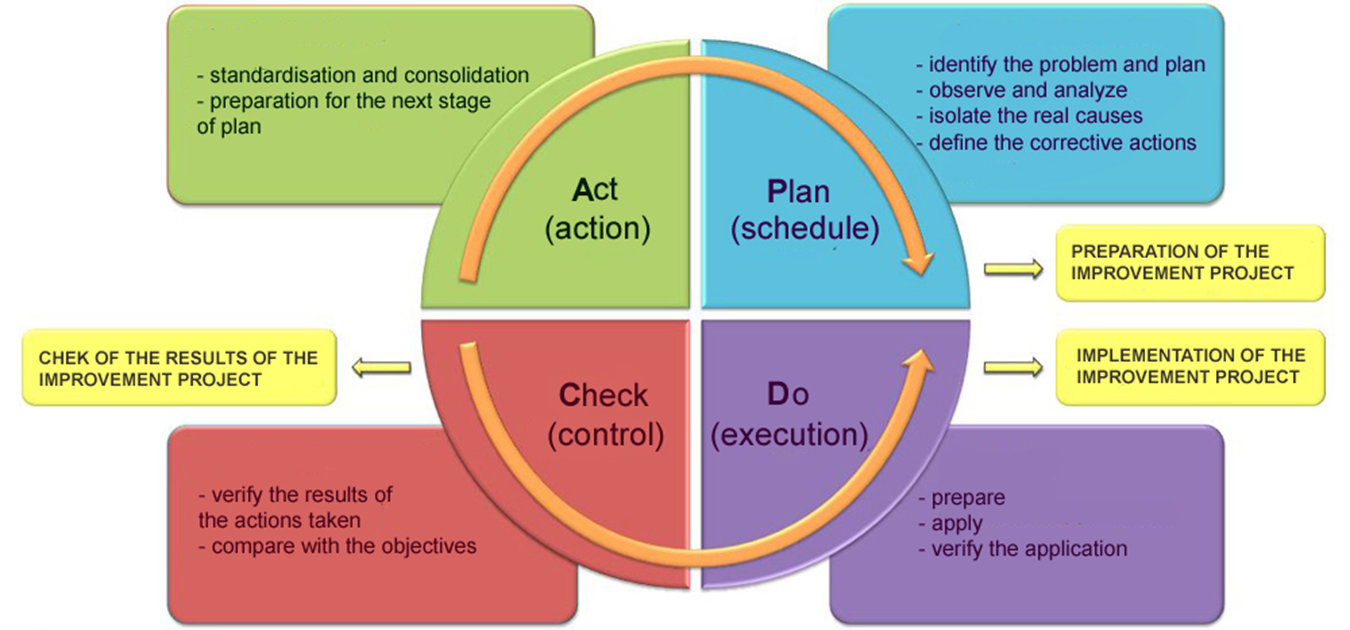
FACTORS AFFECTING QUALITY ASSURANCE IN NURSING CARE
- Lack of Resources: Insufficient resources, infrastructures, equipment, consumables, money for recurring expenses and staff make it possible for output of a certain quality to be turned out under the prevailingly circumstances.
- Personnel problems: Lack of trained, skilled and motivated employees, staff indiscipline affects the quality of care
- Improper maintenance: Buildings and equipment require proper maintenance for efficient use. If not maintained properly the equipment cannot be used in giving nursing care. To minimize equipment down time it is necessary to ensure adequate after sale service and service manuals.
- Unreasonable Patients and Attendants: Illness anxiety, absence of immediate response to treatment, unreasonable and uncooperative attitude that in turn affects the quality of care in nursing.
- Absence of well informed population: To improve quality of nursing care, it is necessary that the people become knowledgeable and assert their rights to quality care. This can be achieved through continuous educational program.
- Absence of accreditation laws: There is no organization empowered by legislation to lay down standards in nursing and medical care so as to regulate the quality of care. It requires a legislation that provides for setting of a stationary accreditation vigilance authority to
- Inspect hospitals and ensures that basic requirements are met.
- Enquire into major incidence of negligence
- Take actions against health professionals involved in malpractice
7. Lack of incident review procedures: During a patient's hospitalization reveal that incidents may occur which have a bearing on the treatment and the patient's final recovery.
These critical incidents' may be
- Delayed attendance by nurses, surgeon, physician
- Incorrect medication
- Burns arising out of faulty procedures
- Death in a corridor with no nurse physician accompanying the patient etc.
8. Lack of good hospital information system:
A good management information system is essential for the appraisal of quality of care.
- Workload, admissions, procedures and length of stay
- Activity audit and scheduling of procedures.
9. Absence of patient satisfaction surveys:
Ascertainment of patient satisfaction at fixed points on an ongoing basis. Such surveys carried out through questionnaires, interviews by social worker, consultant groups, and help to document patient satisfaction with respect to variables that are
- Delay in attendance by nurses and doctors.
- Incidents of incorrect treatment
10. Lack of nursing care records: Nursing care records are perhaps the most useful source of information on quality of care rendered. The records.
- Detail of the patient condition.
- Document all significant interaction between patient and the nursing personnel.
- Contain information regarding response to treatment.
- Have the dates in an easily accessible form.
11) Miscellaneous factors:
- Lack of good supervision.
- Absence of knowledge about philosophy of nursing care.
- Lack of policy and administrative manual
- Substandard education and training.
- Lack of evaluation technique.
- Lack of written job description and job specifications.
- Lack of in-service and continuing educational program.