HOSPITAL
HOSPITAL
The word “hospital “derived from the Latin word hospitalis which in turn derived from french word “hospes” that means “ a host or a guest”or "Hotel" hostel.
- A hospital is a health care institution providing treatment to patients with specialized staff and equipment.
Hospital Definition:-
"A hospital is an integral part of social and medical organization, the function of which is to provide for the population the complete health care, both curative and preventive and whose out patient services reach out to the family and it's home environment the hospital is also a centre for the training of health workers and for biosocial research."
[According to World Health Organization, (WHO)]
A hospital is a health care institution with an organized medical and professional staff, and with permanent facilities that include in- patient beds. Provide medical, nursing and other health related services to patients.
HOSPITAL word means-
- H-Healing
- O-Observation
- S-Supervision
- P-Persuation
- I-Investigation
- T-Treatment
- A-Assurance
- L -Leisure
Objectives -
- Provide optimum health services
- Provide care, cure, preventive service.
- Protect the human rights of clients.
- Provide training for professional
- Provide in service/ continuing education in all disciple professional technical personal.
- Participate/conduct research.
Functions
- Preventive function
- Curative function
- Training function
- Research function
1. Preventive function-
- it is an emerging secondary function for the hospital and concerned with health promotion
- It is geared toward providing the preventive services through a community health center
- It takes an active role to improve the health of the population
2. Curative function-
- it is the primary function of the hospital and concerned with providing patient care
- It refers to any type of care given to the patients by the health team members e.g. physicians, nurses, dietitians.
- Also includes health education to patients
3. Training function-
- It is a secondary function and concerned with providing training and educational courses for the professional and technical personnel who provides health services (e.g. physicians, nurses, dentists, therapist)
4. Research function-
- It is a secondary function and concerned with conducting the health related researches that focus on the improvement of the health and/or prevention of diseases.
Classifications of Hospital -
Hospital have been classified, on the basis of different criteria-
- Based on length of stay
- Based on services
- Based on objectives
- Based on ownership
- Based on size
- Based on management
- Based on system
1. Based on Length of Stay - On the basis of length of stay, hospitals are classified
- Short term care hospitals- In this the client stay in the hospital for a short period only. Eg- Pnemonia
- Long term care hospitals-In this client stays in the hospital for a long time. Eg- Leprosy
2. Based on Services - On the basis of services, hospital are classified into -
- General Hospital-A hospital that provides services for all kinds of illnesses, disease, injuries or deformities. A general hospital shall provide medical and surgical care to the sick and injured, maternity, newborn, and child care.
- Speciality Hospital - A hospital that specialized in a particular disease or condition or in one type of patient.
3. Based on Objectives - On the basis of objectives, hospitals are classified into-
a. Teaching Cum Research hospitals-A hospital to which a college is attached for medical/ Nursing/dental/Pharmacy education. The primary objective is teaching based on the training of doctors and research. Health Care is sencondary objective.
Eg-Medical college hospitals
b. General Hospitals - These hospitals provide treatment for common disease. Eg-Taluk hospitals, PHC
c. Specialized Hospitals - These hospitals provide medical and nursing care in specific area.
Eg-Ophthalmic hospital, heart hospital, Orthopedic hospital
d. Rural Hospitals - Rural hospitals are those located in reral areas permanenty staffed by at least one or more physicians.
e. Isolation Hospitals - This is a hospital in which client requiring isolation or clients suffering from infectious/communicable diseases are taken care of.
4. Based on the Ownership - On the basis of ownership, hospitals are classified into-
- Government Hospital or Public Hospital
- Non-Government Hospital
Government or Public Hospitals - These are run by central or state government or local bodies. These are funded by the government. They provide free care for patients. They can be general or specialized hospitals.
Non-Government Hospitals - They are supported by client's fees or donations. Non- government hospitals are classified into proprietary or non-profit organization. The non- governmental hospital are-
- Private hospitals
- Voluntary hospitals
- Corporate hospitals
- Private Hospitals - They are generally owned or controlled by an individual doctor or group of doctors. They are run on a commercial basis.
- Voluntary Hospitals - They are run by public or private funds on a non-commercial basis
- Corporate Hospitals - They are public limited companies, formed under the companies Act They are run on commercial lines
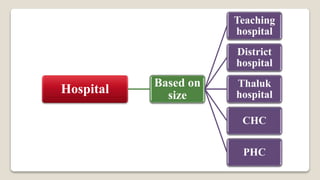
5. Based on Size - On the basis of size, hospitals are classified into the according to bed strength.
- Teaching Hospital - Bed strength 500 or above.
- District Hospital - Bed strength 200 to 300.
- Taluk Hospital - Bed strength 50 to 200
- Community Health Centre (CHC)- Bed strength 30 to 50.
- Primary Health Centre (PHC)- Bed strength 6 to 10.
6. Based on Management - On the basis of management, hospitals are classified into-
- Union Government/Government of India - All hospitals administered by the Governmentof India Eg-Railways, Military
- State Government - All hospitals administered by the State Government
- Local Bodies - These hospitals are administered by local bodies. Eg-Muncipality, Zila parisad, panchayat
- Autonomous Bodies - All hospitals established under special act of parliament or state legislation funded by the central or state government. Eg-AIIMS (New Delhi), NIMHANS (Banglore). PGIMER (Chandigarh)
- Private Hospital - All private hospital owned by an individual or by a private organization. Eg- MAHE. Manipal. Hinduja hospital, Bombay
- Voluntary Hospital - It is a hospital supported in part by voluntary contributions and under the control of local, usually self appointed board of governors. Eg-CMC (Vellore)
7. Based on System - On the basis of system, hospitals are classified into-
- Allopathic hospitals
- Homeopathic hospitals
- Ayurvedic hospital
- Siddha
- Unani hospital
Health Care Team
DEFINITION
Team
"A team means a set of specially prepared persons working together for a common goal." (According to CP Thresyamma)
Health Team
- "Health team consists of particular groups of health care professionals to provide total care for client's" [According to CP Thresyamma]
- It is defined as “ a group of persons who share a common objectives determined by community needs and toward the achievement of which each member of the team contributes in accordance with her/his competence and skills, and respecting the functions of the other.”
Members of Health Care Team
- Physician
- Nurse
- Dietrician
- Physiotherapist
- Social worker
- Occupational Therapist
- Laboratory Technician
- Radiologic Technologist
- Pharmacists
- Physician-Physician is a person who is legally authorized to practice medicine. In hospital setting, the physician is responsible for the medical diagnosis and for determining the therapy required by a person who is ill or injured.
- Nurse - Number of personnel may be involved in health team. The team leader ‘head nurse’ is responsible for delegation of duties to members of her team and care given to the patients.
- Dietrician- Dietitician design special diets and they supervise the preparation of meals according to doctor's prescription.
- Physiotherapist-The physiotherapist provide assistance to patient who has problem related to musculoskeletal system.
- Assessing mobility and strength
- Providing therapeutic measures
- Teaching patients new skills and measures.
- Social worker- Social worker provide assistance to the family and patient. Provide assistance in the problems such as finances, counseling or marital problems, adoption of children etc.
- Occupational Therapist- The occupational therapist assists patient with some impairment of function to gain skills as they relate to activities of daily living and help with a skill that is therapeutic.
- Laboratory Technician- Examines and study specimens such as urine, faeces, blood and discharge from wound.
- Radiologic Technologist- Assists with wide variety of X-Ray procedures.
- Pharmacists- Pharmacists dispense drugs and medications prescribed by physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and dentists.
Additional Members in Community Area
- Health Assistant-They supervise 6 health workers and cover the population of about 30000. Their functions include-
- Administration
- Supervision
- Maintaining human relation skills.
- Community Health Worker -The CHW is a member of the community and play an important role in identifying a community’s problems and in developing solutions.
- ASHA ( ACCREDIATED SOCIAL HEALTH ACTIVIST) - ASHA is a social health activist in community who will create awareness on health. There should be 1 ASHA for 1000 population.
- Village Health Guide- The village health guides are mostly women and this scheme was started on 2nd oct. 1977. They are chosen by the community in which they work. They get training of 200 hours in 3 months.
- Trained Dias - Under the rural health scheme the local dias are trained to improve their knowledge. The training is given at sub centre, PHC & CHC and in community area for 30 days. They play a vital role in propagating small family norm,