COLD APPLICATION
Definition
- Cold application is the application of cold agent, cooler than skin either in a moist or dry form on the surface of the body to relieve pain and body temperature, to anaesthetize an area , to check hemorrhage, to control growth of bacteria, to prevent edema and reduce inflammation.
- Cold application is the application of cold agent, cooler than skin either in a moist or dry form on the surface of skin.
Purpose
- To reduce raised body temperature during high fever & hyper pyrexia or sun stroke.
- To relieve local pain(To anaesthetize an area)
- Cold decrease prostaglandin’s which decreases the sensitivity of pain receptors, and other substances at the site of injury by inhibiting the inflammatory processes.
- To reduce subcutaneous bleeding. Eg- in sprain & contusion.
- To control bleeding. Eg- epistaxis.
- To provide comfort to a patient in extreme hot weather if desired.
- To reduce swelling and inflammation by decreasing the blood flow to the area (vasoconstriction effect).
General Principles of Cold Applications
- Cold causes construction of blood vessels and decrease the blood supply to the area.
- Cold decreases metabolism and the cell activity or growth.
- The end organs of the sensory nerves in the skin convey the sensation of cold; the sensations are interpreted in the brain.
- Woolen materials absorb moisture slowly, but hold moisture longer and colds off less quickly than the cotton materials.
- Moisture left on the skin causes rapid cooling due to evaporation of the moisture.
- Prolonged exposure to moisture increases the skins susceptibility to maceration and skin breakdown.
- After the procedure, dry the part by patting and not by rubbing to remove the moisture.
- During cold applications, protect the client from getting chills. Shivering can raise the temperature.
- Sudden cooling is dangerous to a patient. So, in hyperthermia, the temperature should be brought down gradually and steadily.
Physiological effects.-
- Peripheral vasoconstriction.
- Decreased capillary permeability.
- Decreased oxygen consumption.
- Decreased local metabolism.
- Increased blood viscocity.
- Decreased muscle tone.
- Decreased blood flow.
- Decreased lymph flow.
- Decreased motility of leukocytes.
Therapeutic use of cold application-
- Cold Relieves Pain -Cold decreases the nerve impulse conduction and relieves pain.
- Prevents Gangrene- Cold decreases the tissue metabolism. Cold decreases the effects of tissue anoxia (oxygen lack) & thereby delay the tissue necrosis.
- Prevents edema and reduces Inflammation- It decreases the blood circulation and prevent fluid congestion. Eg – sprains.
- Controls Hemorrhage- it causes vasoconstriction & increases the blood viscosity which helps in the coagulation of the blood and checks hemorrhage.
- Check the Growth of Bacteria -Cutaneous application of cold reduces the tissue temperature and makes the environment less favourable for the growth of the microorganisms.
- Reduces the body Temperature - it is withdrawn from the body by conduction, convection and evaporation. Thus, the body temperature is reduced.
- Cold Anaesthetize an Area - it decrease the sensitivity of tissues and creates a sensation of numbness. Thus it can be used as local anaesthesia for a short period.
Contraindications of Cold Application
- Cold should not be applied on clients who are in a state of shock and collapse.
- When there is edema.
- In disease associated with impaired circulation. Eg – clients with diabetes, arteriosclerosis & neurological disorder.
- When there is muscle spasm.
- When there is decreased sensation. Eg- numbness
- When there is infected wound which are to be dried of the pus or if we intend to promote suppuration.
- When the client is having shivering of having a very low temperature.
Complications -
- Pain
- Hypothermia
- Bluish Discoloration
- Maceration
- Readness
- Skin breakdown
Classification of cold application
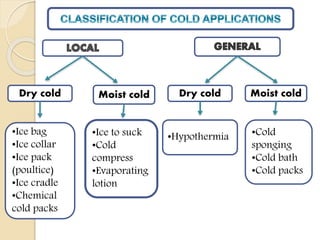
A. Local
- Dry cold
- Ice bag
- Ice collar
- Ice pack
- Moist cold
- Ice to suck
- Cold compress
- Ice cradle
- Chemical cold packs
- Evaporating lotion
B. General
- Dry cold
- Hypothermia
- Moist cold
- Cold sponging
- Cold bath
- Cold packs
Ice Bag -
- Ice kept in a bag
- Covered with cloth and applied on an area
- Temperature <15° C
EQUIPMENTS
| Articles | purpose |
| Ice bag | To provide cold application |
| Bowel | To keep ice cube |
| Duster | To wipe the outside of the jug |
| Towel / ice bag cover | To insulate the coldwater bag |
| Lotion thermometer (if possible) | To check the temperature of the hot water |
| Makintosh | To protect the bed |
| A roll of tape or bandage | To secure the bag |
| Spoon | To take the ice pieces |
Preliminary Assessment of the Patient
- Explain the purpose and procedure to the patient.
- Maintain a comfortable position.
- Prevent draugths by covering the patient with a blanket or a bed cover.
Steps of Procedure.
| Steps | Rational |
| Break the ice into smalll pieces | For easy insertion of ice into bag. |
| Sprinkle sodium chloride | Salt lowers the melting point |
| Check the ice bag for leakage by pouring water into it | To ensure that the bag is in agood working condition. |
| Empty the bag and fill it about 2/3 or with ice. | This makes the bag light in weight. |
| Keep the bag on a flat surface and squeeze out the air. | Air is removed in order that the ice bag can be moulded to the patient’s body. |
| Screw the cap well and wipe it. | To ensure that the bag is not leaking. |
| Put on a flannel cover. | The cover retain cold for more gradual application and it absorbs the water formed by atmospheric condensation. |
| Explain the procedure to the patient. | To gain more co-operation. |
| Spread the mankintosh and the draw sheet. | To protect pillow cover and pillow |
| The ice bag is applied for about half and hour and then it is discontinued for atleast an hour for the recovery period. | To prevent the effect of prolonged exposure to cold |
| Chart the treatment and its effect. | Recording is important for any procedure. |
| Wash the icebag with water and dry it. | For re-use |
| Dry & then powder between the layers of the rubber and store after. | To store it properly |
Aftyer Care of the Client and Articles.
- Remove the ice bag when the treatment completed.
- Dry the area if moist.
- Position the client comfortably on bed.
- Take all the articles to the utility room and replace all the articles.
- Wash hands.
- Records the procedures with dates and times, the area or where it is applied, the purpose of the application & the reaction if any.