Asepsis
Asepsis- Freedom from disease-causing microorganisms.
- "The term asepsis means the absence of disease-producing microorganisms."
- Asepsis is the state of being free from disease causing contaminants (such as Bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites) or preventing contact with micro-organism.
Purposes-
- To prevent cross infection on hospital environment.
- To control infection.
- To ensure patient's comfort, safety and psychological well-being.
Types of Asepsis
There are two types of asepsis-
- Medical Asepsis
- Surgical Asepsis
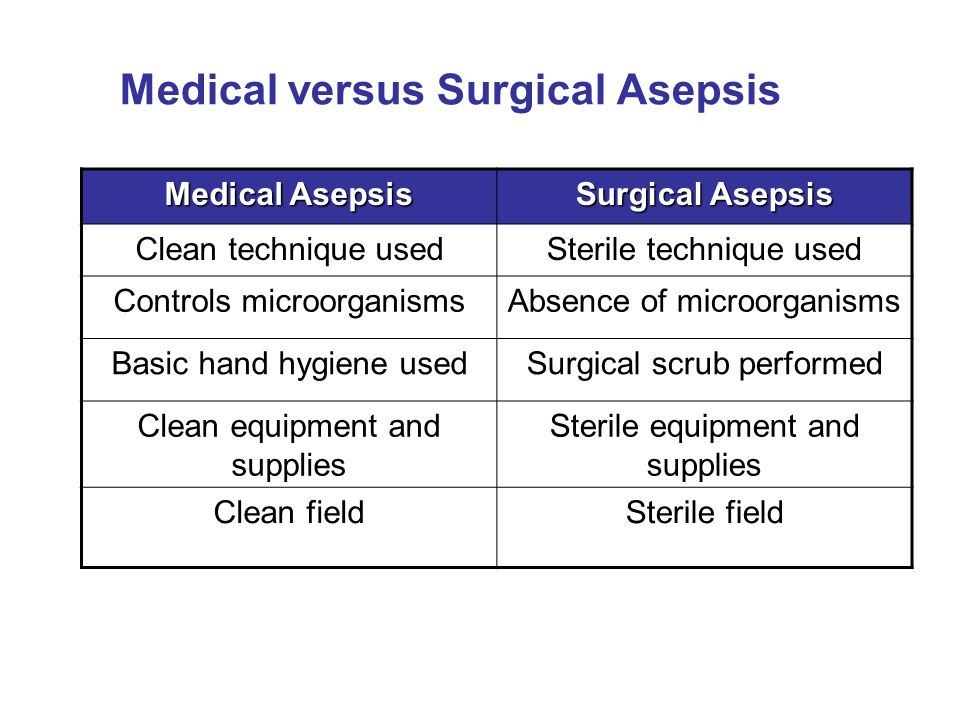
A. Medical asepsis (Clean Technique) -
- Measures used to prevent the spread of organisms from place to place.
- All practices that reduce the Number, growth, transfer and spread of pathogenic microorganisms.
They include hand washing, bathing, cleaning environment, gloving, gowning, wearing mask, hair and shoe covers, disinfecting articles and use of antiseptics.
Cornerstones of Medical Asepsis-
- Know what is dirty
- Know what is clean
- Know what is sterile
- Keep these conditions separate
- Remedy contamination immediately
Principles of Medical Asepsis-
- When the body is penetrated, and natural barriers such as the skin is bypassed ,the patient is susceptible to any microbes that might enter.
- Even though intact skin is a good barrier against microbial contamination, a patient can become colonized with microbes if appropriate precautions are not taken.
- All body fluids from any patient is considered contaminated.
- The healthcare team and the environment can be a source of contamination for the patient.
- Assess each patient to determine if he has an infectious process
- Choose the barrier appropriate to the infectious process
- Isolate the disease not the patient.
- The chain is as strong as the weakest link.
-
Cleanse hands frequently following CDC's hand hygiene guidelines.
-
Keep soiled items and equipment from touching clothing.
-
Do not place soiled bed linens or other items on the floor.
-
Avoid having the patient Cough, Sneeze or breath directly on others.
-
Clean the least soiled items first then the more soiled ones.
-
Dispose off soiled or used items directly into the appropriate containers.
-
Avoid touching your eyes, face and mouth.
B. Surgical asepsis (Sterile Technique)-
- Practices that keep an area or objects free from all microorganisms non pathogenic and pathogenic including spores and viruses.
- Sterile technique is used to prevent the introduction or spread of pathogens from the environment into the patient.
Cornerstones of Surgical Asepsis-
- Know what is sterile
- Know what is not sterile
- Keep the two apart
- Remedy contamination immediately
Principles-
The basic principles of surgical aseptis include-
- Always face the sterile field. Do not turn back or side on a sterile field
- Keep sterile equipment above your waist level or above table level.
- Do not speak, sneeze and cough over a sterile field.
- Never reach across sterile field.
- Keep the unsterile objects away from the sterile field
- Keep the sterile field dry
- The edge of sterile field is considered unsterile
- Handle liquids cautiously near the sterile field or prevent drapes or wrappers from becoming
- Each sterile supply should be clearly labeled as to its contents, time and date of sterilization.
- Never assume that a object is sterile. Always check the sterility expiration date.
- Avoid sweeping and dusting when the sterile objects are opened.
- Put on mask, wash hands, put on gown and gloves before handling sterile supplies.