Bladder Irrigation
Definition
- Bladder irrigation means to flush out the urinary bladder with a liquid.
- Bladder irrigation is defined as a process carried out in order to wash the urinary bladder out. This procedure is performed to wash out the bladder from inside so that the urinary catheter and tubing remain patent and functional.
Purpose
- To cleans the bladder from decomposed urine, bacteria, excess of mucus, pus and blood clots.
- To maintain the patency of the urinary catheter.
- To relieve congestion and pain in case of inflammatory conditions by the application of heat.
- To promote healing.
- To prevent the clot formation in case of bladder surgeries.
- To prevent and treat infections.
- To arrest bleeding
Articles required
A clean tray containing-
- Gloves
- Towel and mackintosh
- Three way retention catheter
- Sterile drainage tubing and bag in place
- Sterile antiseptic swab
- Infusion tubing
- Kidney tray
- IV Stand
Solutions used
- Sterile water
- Normal saline
- Glucose solutions 5%
- Boric acid 2%
- Potassium permanganate 1:10,000
- Acriflavin 1:10,000
- Silver nitrate 1:5000
- Acetic acid 1:400 to treat pseudomonas infection
Types of Bladder Irrigation
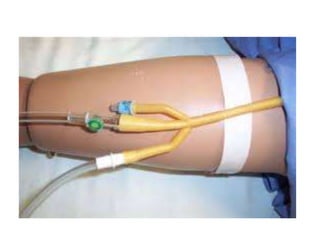
- Continuous bladder irrigation- This method constantly flushes the bladder with fluid using a three-way catheter. This catheter allows fluid to flow in and out of the bladder at the same time. The bladder irrigation fluid flows from a bag similar to an IV, or intravenous, fluid set.
- Intermittent bladder irrigation- This method rinses the bladder as necessary throughout the day. It uses a pump and a port on a two-way urinary catheter set. You or a clinician will hook the fluid up to the port when flushing is necessary. A pump instills the fluid while a clamp keeps the outflow shut. After a certain amount of time, you open the clamp and let the fluid and any debris flow out of the bladder.
- Manual bladder irrigation- This method is also a periodic rinsing of the bladder. However, it does not use a pump. Instead, it uses a syringe to instill the fluid through a catheter. A healthcare professional may perform manual bladder irrigation, or you may receive instructions on how to do it yourself.
General instructions
- Should not be done without written order.
- As far as possible, bladder irrigation are to be avoided.
- The safest and most effective means of irrigating the urinary system is by “internal irrigation”.
- The fluid should be instilled gently and allowed to drain back by gravity.
- If the fluid flows easily into the bladder but fails to return, there is a clot over the eye of the catheter
- In such situation no more fluid is introduced into the bladder but try to dislodge the clot by milking the tubing.
- Practice strict aseptic technique. All the articles that are used for the irrigation must be sterile.
- Wash hand before and after the procedure
- Maintain an accurate records of the amount of fluid used for irrigation and the total amount of urinary drainage. Subtract the total amount of fluid used, from the total amount of urinary drainage to find out the amount of urine secreted by the kidneys.
- For salt restricted patient use dextrose 5% solution instead of normal saline.
- Irrigation are carried out until the return flow is clear.
- The color of the drainage should be checked and recorded. If bleeding takes place stop the procedure and inform to the doctor.
- Record the procedure on the nurse’s record with date and time. Recorded procedure should include- purposes, amount and kind of the solution used, amount and characteristics of the drainage from the bladder, result of irrigation, any complication etc.

| Steps of Procedure | Rational |
| Before beginning the procedure, the nurse has to introduce herself and identify the patient. | To develop rapport and prevent error. |
| Explain the procedure to the patient.
Explain the need and reason for performing the procedure. |
To gain consent and cooperation |
| After comforting the patient, wash the hands to begin the procedure. | To prevent contamination |
| Provide privacy to the patient by using screens. | For privacy of the patient |
| Wear gloves and check the drainage bag for urine. Empty the bag. measure the urine present in it and document the findings. Record the amount of urine and note the appearance. After noting the details, discard the urine along with gloves. | Ensuring the appropriate working of the drainage system and empty to keep record of the output as well as keep the record of the amount instilled shall be same as drained out |
| Wash hands again. The infusion tubing is connected to the irrigation solution.The irrigation infusion tube is flushed and the tip is kept sterile. | To prevent contamination and removal of the air will prevent any complication |
| Wear pair of gloves and the port is cleansed with antiseptic solution using swabs. | To maintain cleanliness of the area and prevent infection |
| Then, the port is connected to irrigation tube. | |
| The irrigation bag along with tubing is connected to the drainage port of urinary catheter. | For instillation of the irrigation solution |
| Remove and discard the gloves. | |
| To initiate a closed continuous irrigation using a three way catheter, the clamp is released from the urinary drainage tubing. The irrigation solution is allowed to flow out of the bladder continuously. | Outflow is obstructed only one-way flow that is toward the bladder is maintained. |
| The flow rate of solution can be regulated as per doctor's orders and can be adjusted accordingly. | To prevent spasm and urgency feeling |
| When the irrigating solution is instilled or allowed to go in the bladder, still the outflow is kept closed for dwelling time period (15-30 minutes or as prescribed by the doctor) | So that the irrigating solution works on microorganism present in the bladder |
| The drained contents are then assessed for color, amount, and cloudiness. | Amount should be same as the amount injected |
| It should be made sure that the amount of drain and the amount entering inside the body should remain equal. | The additional output can be expected due to urine output |
Procedure After care-
- Tape the catheter securely to the thigh
- Assess the patient’s condition and tolerance of the procedure
- Discard all used disposable articles, clean and replace reusable articles
- Wash hands
- Record procedure in nurse’s record.
Complications
- Infection -Urinary tract offer a favourable environment for the multiplication of bacteria because it is dark, moist & warm . Injury to the mucosa of the bladder leads to growth of the bacteria in bladder. Changing the pH value of urine by medication .force of the flow cause injury
- Tissue trauma - During the insertion of the catheter & procedures applied to the bladder , tissue trauma may take place .even the slight movement of the catheter can cause tissue trauma & breakdown.
- Urethral irritation - Symptoms include burning sensation & pain at urethral meatus will be experienced especially by the male pt. due to indwelling
- Bladder spasm or pain - Bladder spasm may occur due to the balloon of an indwelling catheter resting directly on the bladder neck .
- Bladder overdistention