Heart Block
Definition -Heart block is an abnormal heart rhythm where the heart beats too slowly (bradycardia).
In this condition, the electrical signals that tell the heart to contract are partially or totally blocked between the upper chambers (atria) and the lower chambers (ventricles).
Normal conduction pathway- SA node -> atrial muscle -> AV node -> bundle of His -> Left and Right Bundle Branches -> Ventricular muscle
Types-
They are further classified as,
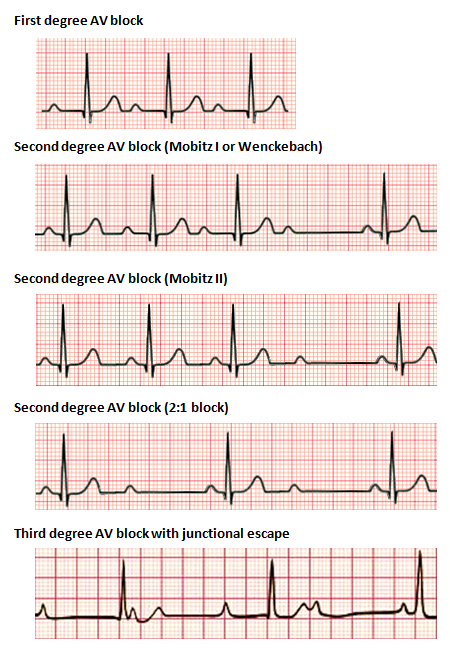
- First degree heart block ( first degree AV block)
- Second degree heart block (second degree AV block)
- Third degree heart block (third degree AV block)
1. First degree heart block ( first degree AV block)-First-degree atrio-ventricular block (AV block), or PR prolongation, is a disease of the electrical conduction system of the heart in which the PR interval is lengthened beyond 0.20 seconds.
Causes of first- degree AV block-
- Intrinsic avascular Necrosis (AVN) disease
- Acute myocardial infarction (MI), particularly acute inferior wall MI Myocarditis
- Electrolyte disturbances (eg, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia)
- Drugs (especially those drugs that increase the refractory time of the AVN, thereby slowing conduction)

First Degree Heart Block (1º)
- SA Node – Normal
- Normal P wave
- AV Node conducts more slowly than normal
- Prolonged PR Interval
- Rest of conduction is normal
- Normal QRS
Significance
- Clinical significance - None
- Treatment-None
- Note – this can progress to 2º or 3º heart block
Second Degree Heart Block (2º)
A. Mobitz Type I (Wenkebach)
B. Mobitz Type II
A. Second Degree Heart Block (2º) Mobitz Type I (Wenkebach)
- Conduction through the AV Node – progressively delayed until a drop beat is seen
- Second-degree atrio-ventricular (AV) block, or second-degree heart block, is characterized by disturbance, delay, or interruption of atrial impulse conduction through the AV node to the ventricles.
Cause-
- Drugs (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, amiodarone)
- Cardiomyopathy
- Rheumatic fever, myocarditis
- Varicella-zoster virus infection
- Rheumatic diseases
- Hypoxia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypothyroidism
- Inferior wall myocardial infarction
- PR Interval prolongs with each beat until a dropped beat is seen The PR Interval is NOT constant
- After each dropped beat, the PR interval is normal and the cycle starts again
Significance
- Clinical Significance - Slight symptoms e.g.. Lethargy, Confusion
- Treatment -Pacemaker if during day &/or symptoms
- No treatment if at night
Note – This can progress to 3º Heart Block
B. Second Degree Heart Block (2º) Mobitz Type II
- Conduction through the AV node is constant.
- PR interval is normal and constant
- Occasionally a dropped beat is seen

Significance
- Clinical significance – This is more significant disease
- Treatment – Pacemaker
Note – This can progress to 3º Heart Block
3. Third Degree Heart Block (3º) (Complete)
Third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, also referred to as third-degree heart block or complete heart block, is a disorder of the cardiac conduction system where there is no conduction through the atrioventricular node.
- Complete failure of the AV Node
- No impulses from Sinus Node will pass through to the ventricles Some part if the conducting system will take over as pacemaker of the heart (even a myocardial cell 10-15 bpm)
- P wave rate – Normal
- Ventricular rate – slow
- Ventricular complex may be broad
- Idioventricular rhythm
- Complete dissociation between P waves & QRS
Significance
- Clinical significance - Symptoms LOC, Confusion, Dizziness, Low BP •
- Can lead to standstill, VT or VF (stokes Adams)
- Treatment - pacemaker
Management
A. Antidysrhythmic Drugs-4 Classes
- Class I- Sodium channel blockers (decrease conduction velocity in the atria, ventricles and His-Purkinje system). Ex:-Procainamide, Quinidine, Lidocaine (Xylocaine), Phenytoin.
- Class II- Beta adrenergic blockers (decrease automaticity of the SA node, decrease conduction velocity in AV node). Ex: - Atenolol, Metoprolol.
- Class III- Potassium channel blockers (Delay repolarization). Ex:- Amiodarone, Dofetilide.
- Class IV- Calcium channel blockers (decrease automaticity of the SA node, delay AV node conduction). Ex:- Diltiazem, Verapamil.
B. Defibrillation:- Defibrillation is a therapeutic procedure in which a direct current (DC) electric shock is passed through the heart to depolarize the cells of the myocardium. When the myocardial cells repolarize, the SA node is usually able to resume the role of heart's pacemaker. The machine used for defibrillation and cardioversion called defibrillator.
C. Electrical Cardioversion:- The procedure of electrical cardioversion same as defibrillation delivered by defibrillator. It is the treatment of choice for patient with hemodynamically unstable ventricular or supraventricular tachydysrhythmias.
D. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)- If patient is at the risk of future life-threatening dysrhythmias. Cardioverter defibrillator is an effective technology to decrease cardia mortality.
E. Pacemaker:- A pacemaker is an electronic device that stimulate the heart muscle through the electrical waves.
Pacemakers are generally used when a patient has slower than normal impulse formation or a rhythmác disturbance that causes symptom.
Nursing Priorities
- Decreased cardiac output related to failure of the heart to pump enough blood to meet metabolic needs of the body as manifested by hypotension.
- Acute chest pain related to decreased blood flow to myo-cardium through coronary arteries.
- Ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased cardiac output as manifestation by syncope.
- Fatigue related to increased hypoxic tissue and slowed removal of metabolic wastes.
- Excess fluid volume
- Ineffective breathing pattern
- Ineffective tissue perfusion
- Activity intolerance
- Impaired airway clearance
NURSING MANAGEMENT
- Assess the high risk patients
- Monitor ECG of the patient
- Assess the family history of heart disease
- Assess the history of smoking and alcoholism
- Monitor lab values frequently especially serum cholesterol levels.
- Assess for CAD
- Monitor vital signs
- Instruct to avoid high fat and oil rich diet