Concept of Health and Illness/Disease
Concept of Health and Illness/Disease
Health
Health is basic human right. The meaning of health is evolved over time. Firstly, the concept of health mainly focus on physical health of individual. In 1977, the 30th World health Assembly decided the main Social target of Governments and WHO, 'Health for All.
- A State of complete physical, Mental and social well being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity.-World Health Organization (WHO)
Concept of Health
Health is evolved over the centuries as a concept from individual concern to world wide social goal and encompasses the whole quality of life.
Changing concept of health till now are-
- Biomedical concept
- Ecological concept
- Psychosocial concept
- Holistic concept
1. Biomedical concept-In biomedical concept of health, the healthy individual is one who is free from disease. Biomedical concept is a traditional concept of health of a person having no disease that person was considered for healthy. This concept is known as biomedical concept and it is based on the germ theory of the disease.
Drawback- Minimized the role of the environmental, social, psychological and cultural determinants of health.
2. Ecological Concept-According to ecological concept of health, health is synchronized with nature. It is equilibrium between the men and environment. If there is any disturbance in this equilibrium can cause the disease in individual.Disease a maladjustment of the human organism to environment.
3. Psychological Concept of Health-As the advancement in social service health is not a biomedical phenomenon. But the health is also influenced by many other facts like-
- Social
- Psychological
- Cultural
- Economic
- Political factors of people concerned.
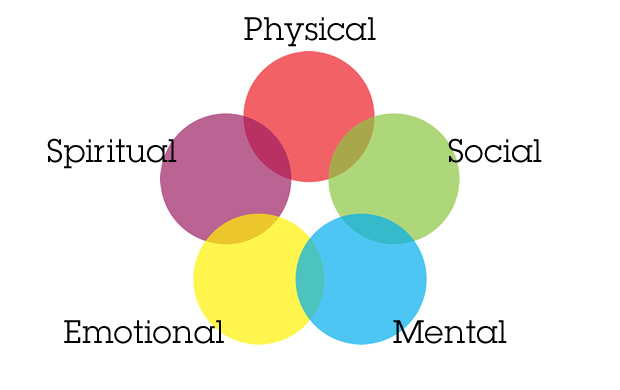
4. Holistic Concept of Health-The holistic model or concept is all complete concept of health. It is an multidimensional concept of health that involves with the dimensions of health like physical, mental emotional spiritual and social. If a person is healthy in all dimensions then that person is considered to be healthy.
Ancient view- Sound mind, in a sound body, in a sound family, in sound environment.
Dimensions of health
- Physical Dimensions
- Mental Social Dimensions
- Spiritual Dimensions
- Emotional Dimensions
- Vocational Dimensions
1.Physical Dimensions -
- Physical health means perfect functioning of the body in which each organ is working in harmony with the maximum capacity.
- Physical health is achieved by the exercise, healthy diet, adequate rest and sleep and no smoking or alcohol intake.
- To maintain proper physical health there is need for taking safety precautions, and regular follow up with the health care providers.
Signs of physical health
- A good complexion.
- A clean skin.
- Bright eyes.
- Not too fatty.
- A sweet breath.
- A good appetite.
- Sound sleep.
- Regular activities of bowels and bladder.
- Smooth, easy, and coordinated bodily movements.
Evaluation of PhysicalHealth
- Self assessment of overall health.
- Inquiry about ill health and risk factors.
- Inquiry in to medications.
- Standardized questionnaire for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
- Clinical examinations.
- Nutritional and dietary history.
- Biochemical and laboratory investigations.
2.Mental Dimensions -
- Mental health refers to cognitive aspect of health.
- Mental health is a state of balance between body and mind . Earlier the body and mind were considered two separate entities.
- But these are interrelated as physical illness can result mental illness and vice versa.
- Any abnormality in brain function is consider to be mentally unhealthy individual, e.g., Alzheimer and dementia. Mentally healthy person has ability to solve the problem, do their work well that leads to good self-estee
Characteristics of mentally healthy person
- Mentally healthy person will be capable of making personal and social adjustment.
- Mentally healthy person is free from internal conflicts.
- He faces problems and tries to solve them intelligently. He has good self control balances rationally and emotionally.
- He knows him self his needs problems and goals.
- He has strong sense of self esteem.
- He serches for identity.
- He lives a well balanced life means able to maintain the balance between work rest and recreation.
3. Emotional Dimensions-
- Emotional health is related to mood. A person who has control over his emotion can express his emotion in a good way are consider to be emotional healthy person.
- Emotional health is closely related to the mental health and is considered as an important element of health.
- Mental and emotional aspects of health are now viewed as two separate entities for human life.
- Cognition is related to the mental health whereas emotional health is related to the feelings of a person.
Emotional health includes-
- An emotionally healthy person has a positive thinking and is capable of coping and adjusting self.
- An emotionally healthy person participates in all the activities which are related to personal growth and his self esteem.
- Emotionally well people have the ability to express feelings freely and manage feelings effectively.
- They are also aware of and accept a wide range of feelings in themselves and others.
4. Spiritual Dimensions-
- Spirituality means in touch with deeper self and exploration the purpose of life, as people believe in some force that transcend physiology and psychology of human beings.
- It includes love , charity, purpose , principles , ethics, intigrity,hope of life.
- Meditations ,prayers, or spiritual gatherings are organized to maintain spiritual health.
5. Social Dimensions-
An individualis socially healthy if he is able to maintain harmonious relationship with other members of society in which he lives. Social health rooted in “positive material environment” and “positive human environment” which is concerned with the social network of the individual.
The social dimensions of health includes-
- Communication
- Intimacy
- Respect
- Equality
- Social functioning
6. Vocational Dimension-
- The choice of profession, job satisfaction, career ambitions and personal performance are all important components of this dimension.
- To be occupationally well, a person is ultimately doing exactly with what they want to do in life and are comfortable with their future plans.
Vocational dimension of health can be assesed by
- Assessing the satisfaction level at job ,
- Facilities attached to the job ,
- Behaviour of the management and administrator and of colleagues at job.
7.Other Dimensions-A few other dimensions also suggested such as -
- Cultural dimensions
- Socio-economic dimensions
- Environmental dimensions
- Educational dimensions
- Nutritional dimensions
- Preventive dimensions
Determinants of Health-
Health is multifactorial. The factors which influence health lie both within the individual and externally in the society in which he or she lives. It is a truism to say that what man is and to what diseases he may fall victim depends on a combination of two sets of factors - his genetic factors and the environmental factors to which he is exposed. These factors interact and these interactions may be health-promoting or deleterious. Thus, conceptually, the health of individuals and whole communities may be considered to be the result of many interactions.
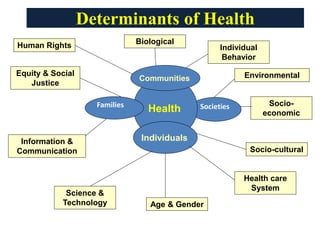
- Biological
- Behavioural
- Environmental
- Socio-economic
- Health system
- Sociocultural
- Ageing of the population
- Science and technology
- Information and Communication
- Gender
- Equality and social justice
- Human rights
1. Biological Determinants- Genetic -Gene’s characteristics inherited from parents, make a person more likely or less likely to develop certain health problems, such as heart disease.
Genetics inheritance plays a part in determining lifespan, healthiness and the likelihood of developing certain illnesses. Others like-
- Chromosomal anomalies
- Errors of Metabolism
- Mental retardation
2. Individual Behavioral and Life style
- Individual behavior and life style affects the health status.
- Life style denotes “ the way that people live”, reflecting a whole range of social values, attitudes & activities.
- Health is determined by its Life style, Culture, Behavior, Personal habits.
Healthy Life Styles
- Adequate nutrition
- Enough sleep
- Sufficient physical activity
Harmful Life Styles
- Lack of sanitation
- Poor nutrition
- Personal hygiene
- Elementary Human habits, customs and cultural patterns Individual Behavioral and Life style
3.Environmental
- It was Hippocrates who first related disease to environment, e.g., climate, water, air, etc.
- Environment is classified as "internal" and "external".The Internal environment of man pertains to "each and every component part, every tissue, organ and organ-system and their harmonious functioning within the system". Internal environment is the domain of internal medicine.
- The external or macro-environment consists of those things to which man is exposed after conception. It is defined as "all that which is external to the individual human host"
Internal Environment( Cells, tissues, organs ) - Harmonious functioning
External Environment-
- Physical
- Biological
- Psychosocial
Domestic (Micro) Environment: Way of living, eating habits, smoking, drinking, use of drugs etc. Environmental Determinants
4. Socio-Economic Determinants-Income and social status have a significant impact on health status. Like higher income and social status are linked to better health. The greater the gap between the richest and poorest people, the greater the differences in health.
Socio-economic conditions depends upon-
- Per capita Income-The economic status determines- The purchasing power, Standard of living, Quality of life, Family size and the pattern of disease & Deviant behaviour in the community. Upper socio-economic groups may also be a contributory cause of high rates of coronary heart disease, diabetes and obesity.
- Education-Major factor influencing health status. • Especially female education. • Illiteracy can be a major cause of poverty, malnutrition, ill health, high infant and child mortality rates. • low education levels are linked with poor health, more stress and lower self- confidence
- Nutrition
- Employment-The very stateof being employed in productive work promotes health, because the unemployed show a higher incidence of ill health and death.
- Housing
- Political system-Mainobstacle to the implementation of health technologies are not technical, but rather political.
5. Health Care System Determinants-Those who have good access to health services, which can prevent and treat the disease condition influences the health of other Community people.
- Immunization of children
- Provision of safe drinking water
- Care of pregnant and children
- Equitably distributed
- Accessible
- Primary Health care
6. Socio-Cultural Determinants -Many customs tradition beliefs and value of a family can affect the health in both way either positively or negatively, e.g., practice of giving Honey after child birth is wrong practice whereas providing mother a good diet after child birth can effect the health in both ways.
7. Ageing of the population
- As people age, they become more susceptible to disease and disability. For example : - Heart disease, stroke, and cancer have been the leading chronic conditions that have had the greatest impact on the aging population
- Under five child are more susceptible for diarrhea, ARI and other specific diseases.
8. Science and technology-
- Science contributes to understanding the causes, mechanisms, and treatments of diseases. It enables evidence-based medicine and public health policies.
- Example-Vaccines – Scientific research led to the development of vaccines for diseases like polio, measles, COVID-19, etc. Vaccines prevent outbreaks, reduce mortality, and improve overall life expectancy.
- Technology includes tools, machines, and systems developed to solve health problems or improve quality of life. It affects healthcare delivery, diagnostics, treatment, health monitoring, and health education.
- Science provides the knowledge base, and technology applies that knowledge to real-world healthcare settings.
- Example Combined-The discovery of insulin (science) and the development of insulin pumps (technology) together revolutionized diabetes management.
9. Gender
- Men and women suffer from different types of diseases at different ages and some of these diseases affect men and women differently.
- Women face higher rates of diseases in some areas such as breast cancer, osteoporosis and auto-immune diseases.
- In the aspect of nutrition, reproductive health, violence women contract the disease more whereas life styles, occupational problems are more seen among men.
10.Information and Communication-Information and Communication are critical social determinants of health. They influence how individuals access, understand, and use health-related knowledge to make decisions. These determinants affect health literacy, health behaviors, access to care, and health outcomes.
11. Equality and social justice-Equality and social justice are critical determinants of health—they shape the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. When these principles are upheld in society, they contribute to better health outcomes for all. When they are lacking, health disparities and systemic inequalities persist.
Equality in Health
- Means providing everyone with the same resources or opportunities to achieve optimal health.
- However, equality doesn’t always result in fairness—some people need more support to reach the same health outcomes as others.
Social Justice in Health
- it’s about removing barriers and addressing the root causes of health inequities (like poverty, discrimination, and unequal access to care).
12. Human rights-A human rights-based approach to health:
- Holds governments accountable for ensuring access to the determinants of health.
- Empowers individuals and communities to claim their rights.
- Addresses root causes of health inequities (e.g., poverty, racism, gender inequality).
- Promotes dignity, equality, and respect in healthcare settings.