Abdominal Examination
Abdominal Examination-
Aims of Abdominal Examination
Abdominal examination should be done to:-
- Observe signs of pregnancy;
- Assess foetal size and growth;
- Assess foetal health; and
- Diagnose the location of the foetal parts.
-
To detect any deviation from normal.
Steps for Abdominal Examination
1. Inspection
2. Palpation
3. Auscultation
1. Inspection
By inspection, you will come to know the size of the abdomen and stretch marks or striae, and linea nigra and any surgery scar.
Inspection (5s)
a.Shape:-
- Note contour -is it round, oval, irregular or pendulous?
- Longtudinal, ovoid in primigravida
- Rround in multipara.
- Broad in transuerse lie.
b. Size:- Should correspond with the supposed period of gestation
c. Skin: - The dark line of pigmentation which is lineanigra is seen any rash?
d. Strae gravidarum
e. Scar - Any operation scar(c/s)
2.Palpation
Uterine fundus is palpated at each check up to corroborate normal foetal growth as
- 14th week – 2.5 cm above symphysis pubis
- 18th week – 4 cm below umbilicus
- 24th week – At level of maternal umbilicus
- 28th week – At lower 1/3rd distance between umbilicus and ensiform cartilage
- 32nd week – At lower 2/3rd distance between umbilicus and ensiform cartilage
- 36th week – reaches below sub costal arch.
- 40th week – comes lower below 36th week but lies above 32nd week.
First Step — Fundal palpation
Purpose- To know lie and presentation.
Palpation of height of fundus by outstretched left palm.
Second Step — Fundal grip — Midwife faces the woman’s face. Uterine fundus is palpated by both palms to determine soft pole of foetus or hand foetal head is felt
Third Step — Lateral grip —Lateral Palpation: (2nd Leopled maneuver)
Purpose-To know lie and position Uterus is felt to determine foetal back on one side and irregular limbs on the other in vertex and breech presentation.
- Place your hands on either side of the middle of her abdomen. Push gently with one hand while holding the other hand firm to steady the uterus; alternate the pressure between your two hands.
- If you feel the round, hard shape of the baby's head at one side, and the fundus feels empty, it may be a transverse lie and you should refer the mother urgently.
Pelvic grip: (3rd Leopoled Maneuver)
Purpose -To Know Presentation & Attitude
Foetal pole at lower part of uterus is palpable by both palms. Hard foetal head is felt in vertex, soft breech in breech presentation.
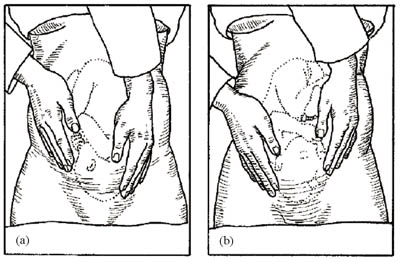
Pawlik’s grip: Foetal head–(4th Leopard Maneuver) In vertex presentation. Foetal head is gripped at lower part of pregnant uterus. This palpation confirms palpation by pelvic grip.
The purpose of the fourth manoeuvre (also known as Pawlick's grip) is to help determine whether the fetal head (in a cephalic presentation) has descended into the mother's pelvis and engaged in the cervix.

3.Auscultation (Hearing of Foetal Heart Sound)-
Foetal heart sound is heard by stethoscope at the site of foetal back on the spino-umbilical line or on the flanks in vertex presentation. Foetal heart rate heard at 120-140/min ensures foetal well-being.
Method:
- Use Pinards stethoscope
- hand should not touch it while listening,
- ear must be in close from contact with stethoscope,