Fungi
Fungi-
A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms.
Mycosis-
A fungus infection is called mycosis. Human diseases caused by fungi are collectively called as mycotic diseases or mycoses. (A disease cause by mycosa or myotic organism.)
Sources of Mycoses
The cutaneous infections are spread from person to person by towels, beddings, clothings, etc. and sometimes even become epidemic. Many fungi are normal inhabitants of the human skin but under some unusual circumstances become pathogenic. The sources of systemic mycoses are fungi of soil. These are present in the environment and are acquired by inhalation. Systemic infections never spread from person to person.
Classification of Mycoses-Mycoses are classified into four groups-
- Superficial Mycoses
Surface Mycoses -
- Tinea versicolor
- Tinea nigra
- Piedra
Cutaneous Mycoses -
- Tinea pedis
- Tinea corporis
- Tinea favosa
- Tinea capitis
- Tinea barbe
- Tinea unguium
- Tinea cruris
- Candidiasis
- Subcutaneous Mycoses-
- Mycetoma
- Chromomycosis
- Phycomycosis
- Rhinosporidiosis
- Sporotrichosis
- Systemic Mycoses-
- Cryptococcosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Opportunistic Mycoses
- Aspergillosis
- Zygomycosis
- Superficial Mycoses-
Superficial Mycoses are strictly surface infections.
These are of two types
- Surface Mycoses
- Cutaneous Mycoses
Surface Mycoses-
The fungi which live exclusively on the dead layers of the skin and its appendages (hair and nails) cause surface mycoses. Examples are Tinea versicolor, Tinea nigra and Piedra.

- Tinea versicolor- It is a chronic infection of the horny layer of the epidermis caused by a yeast like fungus. The cells are oval and divide by budding. It produces cosmetic effects such as brownish discolouration of the skin. The commonest sites involved include chest, back, abdomen, neck and upper arm.

- Tinea nigra- It is an infection of the palms producing black or brown lesions. These lesions appear as irregular flat dark brown or black discoloured areas. Skin scrapings show brownish branched septate hyphae and budding cells.

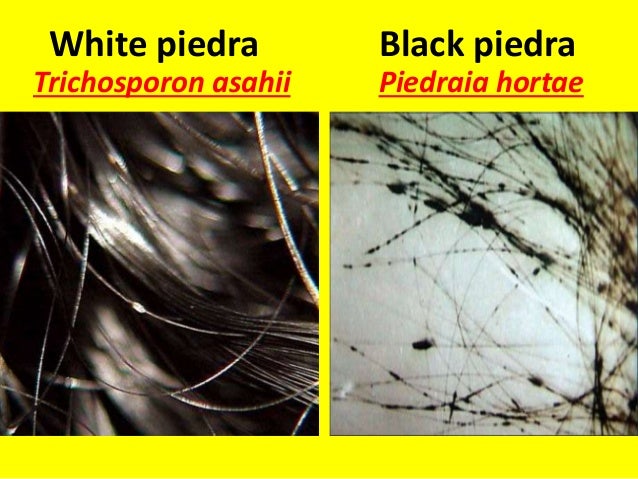
- Piedra (White or Black Piedra)- It is an infection of the hair and produces irregular white or black hard nodules on the hair shaft.

Cutaneous Mycoses-
These infections attack all parts of the outside of the body. They are generally confined to the superficial cornified layer (keratin) of the skin and its appendages, and are called dermatomycoses or dermatophytoses or Tinea ringworms. These are caused by dermatophytes (dermatophyte fungi) and are classified into three genera, viz. Trichophyton, Epidermophyton and Microsporum. Cutaneous infection is also caused by a type of yeast Candida albicans.
The Three Genera
- Trichophyton -It infects skin, hair and nails and produces a characteristic honey comb appearance on scalp. The spores are arranged along the hyphae or sometimes in clusters. These destroy keratin of hair giving rise to broken hair and may cause ringworm of the scalp (Tinea capitis), foot (Tinea pedis), skin (Tinea cruris), beard (Tinea barbe) and nails (Tinea unguium).

- Epidermophyton -It invades skin and nails but not hair. This fungus contains only one species E. floccosum and infects only man. It is one of the commonest of all the dermatophytes in cutaneous infections. A typical colony consists of a mycelium with large club shaped spores. It is largely responsible for Tinea barbe, Tinea capitis, Tinea pedis, Tinea unguium.
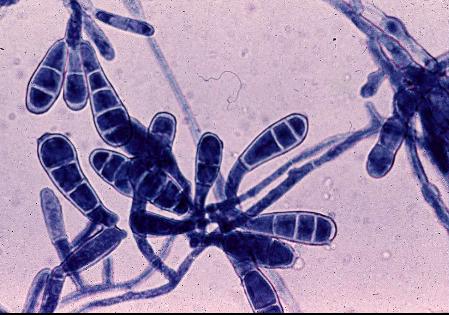
- Microsporum - It invades hair and skin but not nails. It is the most common cause of ringworm of the scalp but it may also give rise to ringworms in other parts of the body. A typical colony consists of mycelium with large thick walled spindle shaped spores. It penetrates the hair and extends down the shaft as fine filaments. Microsporum causes hair and skin infections.
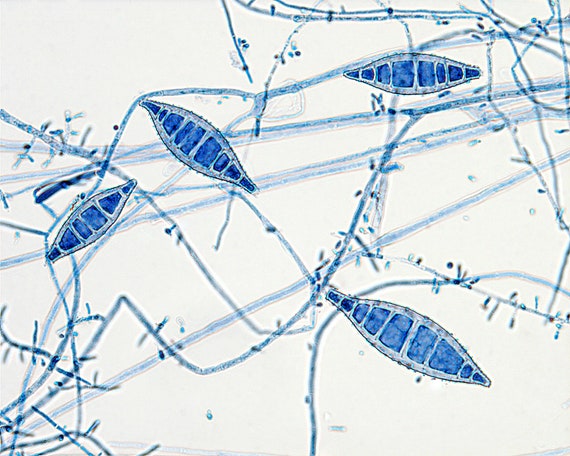
Ringworm Diseases
These are the diseases caused by any one of the following three dermatophytes, viz. Trichophyton, Epidermophyton and Microsporum and are classified clinically on the basis of the site involved. These are of several types-
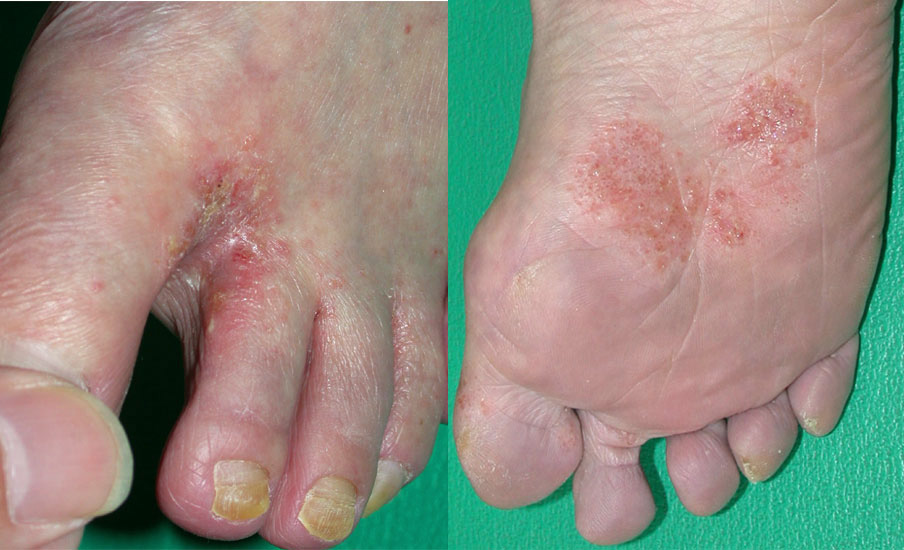
- Tinea pedis (Ringworm of the feet, athlete’s foot)- It is the infection of the skin between the toes and sole of the foot and sometimes similar areas on the hand. ‘Soft corn’ between fourth and fifth toes is a very common chronic infection. It is common in people who wear socks and closed shoes.

- Tinea corporis (Ringworm of the smooth skin)-It appears on the smooth skin and is more common in children than adults. It is often acquired from pet dogs or from farm animals.

- Tinea favosa (Honey Comb Ringworm)- It is also called favus and often injures the hair follicle causing permanent areas of baldness. It may also give rise to cupshaped crusts on the smooth skin. It often occurs as epidemic in children in camps.

- Tinea capitis (Ringworm of the scalp)- It is common in boys of school age. The infected hair will have a coloured glow under the lamp.
- Tinea barbae (Ringworm of the beard)- It is also known as barber’s itch. It is a chronic infection of the beard and spreads by the use of improperly disinfected shaving equipment.

- Tinea unguium (Ringworm of the nails)- It is an infection of the finger nails or toe nails.
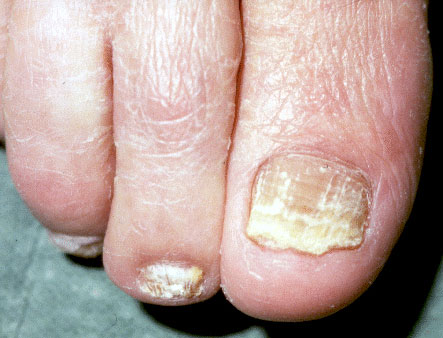
- Tinea cruris (Ringworm of the groin)-It involves the skin and spreads by using used towels and borrowing clothes.

Candidiasis (Moniliasis)-
The infection caused by Candida is called Candidiasis (Moniliasis). There are several species of Candida found in man of which Candida albicans is responsible for almost 90% of the human infections. Its relationship to disease is hard to determine as it is so often found in the normal flora of mucous membrane of the mouth, intestinal tract and vagina as harmless saprophytic yeast like fungus with no disease.
It occurs in two forms-
- Spherical or oral budding cells
- Elongated filamentous cells (joined end to end) with blastospores and chlamydospores in clusters.
It occurs both in culture as well as in tissues and colonies are smooth, creamish white with a yeasty odour. Infection on the mucous membrane of the mouth produced by Candida albicans- is called thrush (white creamish patches on the tongue) common in newborn infants in hospital nurseries.
Moniliasis of the vagina- is common in a person with diabetes in pregnant women and in women on birth control pills.
C. albicans- can infect skin around the toes, fingers and nails and can also cause chest disease. Candida infection is mostly confined to the skin but if the resistance of the person is low or the normal bacteria are reduced by the use of excessive medication with antibiotics, Candida cells, which are normally present on the skin, increase rapidly and cause a very serious and destructive skin infection. It can also secondarily invade an organ such as lungs, heart, brain, etc. causing systemic infection.
Subcutaneous Mycoses-
Subcutaneous mycoses are caused by fungi present in soil or decaying vegetation. The microbes enter the subcutaneous tissues, destroy cells and form sinuses. The lesions are localised and slowly spread via lymphatics. Subcutaneous mycoses include mycetoma, phycomycosis, chromomycosis, rhinosporidiosis and sporotrichosis.
- Mycetoma (Mycotic Mycetoma)-Mycetoma is a localised chronic infection of subcutaneous tissue and often affects the foot. This disease occurs mostly among bare footed persons. The organisms enter the body, burrow into the deeper tissue and lead to swelling, abscess and tumour of foot. The organisms multiply in the centre of the tumour as a colony and finally the tumour bursts and the organisms discharge a peculiar fluid with pus and black, white or brown granules. This disease mostly occurs in India in Tamilnadu especially in Madurai district where the incidence of foot disease is very high.
- Phycomycosis-Phycomycosis is also known as zygomycosis or Mucor Mycosis. Phycomycosis is a general term used for a group of infections caused by several lower fungi such as Rhizopus, Mucor, Absida, etc. In the earlier stages it involves nasal mucosa, spreads to nasal sinuses and later painless subcutaneous nodules are formed on the large area of the body sometimes involving the whole limb. The fungus is a saprophyte and infection is acquired by insect bite.

- Chromomycosis-It is a chronic infection of the subcutaneous tissue and skin producing warty lesions. The fungus enters the body through a wound and forms a chronic granuloma on the skin usually on the legs. The lesions show the presence of round and irregular dark brown bodies.
- Rhinosporidiosis-Rhinosporidiosis is a chronic disease and forms granuloma on the skin. Wart like lesions are formed normally in the mucous membrane of nose, mouth or eye. Very rarely other mucosal sites are involved. It is more common in India and Sri Lanka, though the disease was first identified in Argentina. Thousands of endospores are present embedded in connective tissue.

- Sporotrichosis-It is caused by Sporotrichum (Sporothrix) schenkii and occurs as a chronic infection. Human acquires this infection from infected plants. The organisms enter the body through the wounds. The wounds do not heal and form nodules on the skin and subcutaneous tissue. These nodules breakdown and form ulcers. The fungus spreads through lymphatics upto lymph nodes. The upper limb is usually most affected. It is dimorphic fungus showing yeast phase in tissue and cultures, while mycelial phase is found in nature as well as in culture. Sporothrix hyphae bear flower like clusters of pear shaped spores at the tips of the branches as well as along the sides of the hyphae.

Systemic Mycoses-
Systemic mycoses due to primary pathogens originate primarily in the lungs and may spread to many organ systems.
Systemic Mycoses are caused by fungi of soil and are acquired by inhalation. They grow either as yeasts or filaments. They are rarely seen in India. These include Cryptococcosis, Histoplasmosis, etc.
- Cryptococcosis (Torulosis)-This disease is caused by yeast like organism cryptococcus neoformans also known as Torula histolytica. These organisms are spherical budding cells and have thick capsules around them. The colonies are smooth brownish and do not develop hyphae. It is a saprophytic fungus and has been found in bird droppings, soil, normal skin and faeces. When it enters the body through the skin or lungs it may invade the tissues, lymph nodes, bones and other organs. In most cases, it spreads to the central nervous system causing Torula meningitis, which can be diagnosed by finding encapsulated cells in the spinal fluid. Cryptococcosis infection occurs throughout the world but is seen most frequently in patients with AIDS.
- Histoplasmosis-Soil-Enriched with Bird droppings and Bat droppings Spread through inhalation of spore. Histoplasmosis infection is caused by Histoplasma capsulatum. It is unique among pathogenic fungi as it is an intracellular parasite, which attacks the reticulo-endothelial system. These are small yeast like organisms and the mycelial phase is found in culture. The spores are present in air, water, soil of farm buildings and infection is acquired by inhalation of these spores. Some persons develop a pulmonary disease, more or less similar to tuberculosis. The ulcerating lesions may develop in the nose and mouth and there is enlargement of the spleen, liver and lymph nodes.
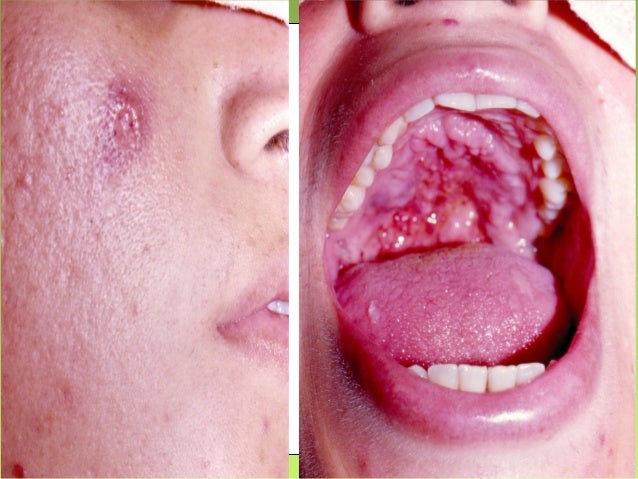
Opportunistic Mycoses-
There are several saprophytic fungi in the environment, which usually do not produce disease, but under special conditions when a person’s immunity is low or one has been on constant use of drugs, antibiotics, steroids etc., these may cause acute or fatal infections. Some of these infections are mentioned below:
- Aspergillosis-It is a disease caused by a grey green mould Aspergillus fumigatus causing Aspergillus asthma or bronchopulmonary aspergillosis diseases in humans. The infection may be mild or may cause ulcers on the external ear and perforate into the middle ear. It may also cause pulmonary sinus or subcutaneous tissue infection.
- Zygomycosis (Mucoromycosis)-Three genera of zygomycetes, viz Mucor, Rhizopus and Absida, which are normally nonpathogenic but under special conditions become pathogenic and cause zygomycosis infection in humans. The infection may confine to lungs or may spread to brain and other organs and sometimes may be even fatal.
MYXOTOXICOSIS
Toxin produced by Fungi is known as Myxotoxin. Many fungi produce poisonous substance Myxotoxin and cause Myxotoxicosis disease, i.e. Mycotic poisoning in man. Myxotoxins are mostly produced by poisonous mushrooms and can cause active or chronic intoxication, which can severely damage the organs such as liver, kidney, and bone marrow.