Nursing process
Nursing process-
Nursing process is a systematic method of providing care to clients.
Definition-
- Nursing process is a framework that enables the nurse and the client together to resolve health related problems of the client in a systematic, organized and logical way.
- Nursing process is a critical thinking process that professional nurses use to apply the best available evidence to caregiving and promoting human function and responses to health and illness.
(American Nursing Association, 2010)
- The nursing process is a systematic method of planning and providing individualized nursing care.
- Nursing process is a method of problem Identification and problem solving.
Purposes-
- It provides a framework within which nurses can identify client’s health status and provide quality care and checks its outcomes through evaluation.
- It helps in providing organized priority based care.
- It encourages clients and family participation in care.
- It helps in rendering individualized care.
- It avoids unnecessary (duplication of) nursing actions thus saves time.
- It serve as record of documentation of the care provided.
Characteristics of nursing process-
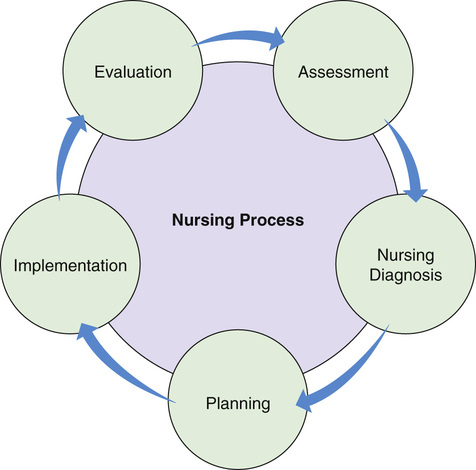
- Cyclical and continuous
- Dynamic nature
- Individualized and Client centeredness
- Focus on problem solving and decision making
- Universal applicability
- Use of critical thinking and clinical reasoning
- Interpersonal and collaborative style
- Prioritizing the needs
Steps-
Nursing process consists of the following steps-
- Assessment
- Nursing Diagnosis
- Planning
- Implementation
- Evaluation
A. Assessment-
Assessment is the foundation step of nursing process. It consists of systematic and orderly collection of information pertaining to and about the health status of the client. The information obtained helps to make nursing diagnosis and to develop a plan of care. Information’s are obtained by data collection.
Definition
Assessment is the systematic and continuous collection, organization, validation, and documentation of data (information).
Types of assessment
The four different types of assessments are-
- Initial nursing assessment
- Problem-focused assessment
- Emergency assessment
- Time-lapsed reassessment
1. Initial nursing assessment- Performed within specified time after admission. To establish a complete database for problem identification. Eg: Nursing admission assessment
2. Problem-focused assessment - To determine the status of a specific problem identified in an earlier assessment. Eg: hourly checking of vital signs of fever patient
3. Emergency assessment- During emergency situation to identify any life threatening situation. Eg: Rapid assessment of an individual’s airway, breathing status, and circulation during a cardiac arrest.
4. Time-lapsed reassessment- Several months after initial assessment. To compare the client’s current health status with the data previously obtained.
A. Collection of Data
Data collection is the process of gathering information about a client’s health status. It includes the health history, physical examination, results of laboratory and diagnostic tests, and material contributed by other health personnel.
Types of Data-
- Subjective data- What the client says about himself. also referred to as symptoms or cohort data, are clear only to the person affected and can be described only by that person. Itching, pain, and feelings of worry are examples of subjective data.
- Objective data- What the health practitioner observes about the client. also referred to as signs or overt data, are detectable by an observer or can be measured or tested against an accepted standard. They can be seen, heard, felt, or smelled, and they are obtained by observation or physical examination. For example, a discoloration of the skin or a blood pressure reading is objective data.
Sources of Data
Sources of data are primary or secondary.
1. Primary - It is the direct source of information. The client is the primary source of data.
2. Secondary- It is the indirect source of information. All sources other than the client are considered secondary sources. Family members, health professionals, records and reports, laboratory and diagnostic results are secondary sources.
The methods of data gathering are the following-
- The interview- There are two approaches to interviewing-
- Directive-The directive interview is highly structured and directly ask the questions. And the nurse controls the interview.
- Nondirective- A nondirective interview, or rapport building interview and the nurse allows the client to control the interview.
- The nursing history
- The physical examination - Observation and measurement
- The psychological and mental health examination -Psycho-Social measurement
- Laboratory Data
B. Organization of data- The nurse uses a format that organizes the assessment data systematically. This is often referred to as nursing health history or nursing assessment form.
C. Validation of data- The information gathered during the assessment is “double-checked” or verified to confirm that it is accurate and complete.
D. Documentation of data- To complete the assessment phase, the nurse records client data. Accurate documentation is essential and should include all data collected about the client’s health status.
B. Nursing Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the second phase of the nursing process. In this phase, nurses use critical thinking skills to interpret assessment data to identify client problems.
"A clinical judgment concerning a human response to health condition/ life processes, or a vulnerability for that response, by an individual, family group, or community"
(NANDA)
Purpose of Nursing Diagnosis
- Identify how and individual, group or community responds to an actual or potential health and life processes
- Identify factors that contribute to or cause health problems (etiology).
- Identify resources or strengths the individual, group or community can utilize to prevent or resolve.
Components of a NANDA-
A nursing diagnosis has three components-
- The problem and its definition-The problem statement describes the client’s health problem.
- The etiology-The etiology component of a nursing diagnosis identifies causes of the health problem.
- The defining characteristics--Defining characteristics are the cluster of signs and symptoms that indicate the presence of health problem.
The diagnostic process involves processing the data by classification interpretation and validation. Writing nursing diagnostic statement is the basis of identifying client’s problems and strengths. The health problem and the etiological factor are reflected in the formulation of diagnostic statement. The diagnosis is verified with the client and documented.
Status of the Nursing Diagnosis
The status of nursing diagnosis are actual, health promotion and risk.
- An actual diagnosis is a client problem that is present at the time of the nursing assessment.
- A health promotion diagnosis relates to clients’ preparedness to improve their health condition.
- A risk nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgement that a problem does not exist, but the presence of risk factors indicates that a problem may develop if adequate care is not given.
Formulating Diagnostic Statement-
The basic three- part nursing diagnosis statement is called the PES format and includes –
- Problem (P) – Statement of the client health problem.
- Etiology (E) - causes of the health problem.
- Sign and symptoms(S)-Characteristics manifested by the client.
Example-
1. Nursing diagnosis- Fever related to post-operative infection as evidenced by temperature 100°f, body ache and body is hot to touch.
2. Acute pain related to abdominal surgery as evidenced by patient discomfort and pain scale.
| Problem | Etiology | Signs/Symptoms |
| 1. Fever | Post-operative infection | Temp-100.°f, body ache, body is hot to touch. |
| 2. pain | surgery of abdomen | pain scale and discomfort of patient |
Nursing Diagnosis and a Medical Diagnosis
| S/N | Nursing Diagnosis | Medical Diagnosis |
| 1 | A nursing diagnosis is created by a nursings | A medical diagnosis is made by physician. |
| 2 | Focused on care. | Mainly focused on etiology. |
| 3 |
Diagnosis may change from day to day as the patient's responses change. Example- 1. Ineffective breathing pattern related to bronchitis as evidenced by irregular breathing. 2. Fluid volume deficit related to dehydration as evidenced by poor skin turgor |
Diagnosis remains the same for as long as the disease. Example- 1. Myocardial infraction. 2. Cancer cervix.
|
| 4 | Identification- A nursing diagnosis identifies the patient’s present signs and symptoms | Identification- while the medical diagnosis identifies the pathology which causes the patient’s illness. |
| 5. | Main feature- A nursing diagnosis helps to focus on the patient’s physical and psychological reactions | Main feature-The medical diagnosis helps to focus on the patient’s actual illness. |
C. Planning-
- Planning involves decision making and problem solving.
- It is the process of formulating client goals and designing the nursing interventions required to prevent, reduce, or eliminate the client’s health problems.
TYPES OF PLANNING
- Initial Planning-Planning which is done after the initial assessment.
- Ongoing Planning-It is a continuous planning.
- Discharge Planning-Planning for needs after discharge.
Planning process Planning includes;
- Setting priorities-The nurse begin planning by deciding which nursing diagnosis requires attention first, which second, and so on. Nurses frequently use Maslow’s hierarchy of needs when setting priorities.
- Establishing client goals/desired outcomes-After establishing priorities, the nurse set goals for each nursing diagnosis. Goals may be short term or long term
- Selecting nursing interventions and activities-A nursing intervention is any treatment, that a nurse performs to improve patient’s health.
- Writing individualized nursing interventions on care plans-
- After choosing the appropriate nursing interventions, the nurse writes them on the care plan.
- Nursing care plan is a written or computerized information about the client’s care.
Outcomes/goals are written from the diagnostic statement in terms of client’s behaviour that are desired to be achieved by the nurse in the limited time. The characteristic features of outcomes are:
- Client centered
- Observable and measurable
- Time limited and realistic.
The areas in which outcomes are written include-
- Appearance and functioning of the body,
- Specific symptoms,
- Knowledge,
- Psychomotor skills and emotional status.
Types of Nursing Interventions
- Independent interventions are those activities that nurses are licensed to initiate on the basis of their knowledge and skills.
- Dependent interventions are activities carried out under the orders or supervision of a licensed physician.
- Collaborative interventions are actions the nurse carries out in collaboration with other health team members
D. Implementation-
Implementation involves preparation for executing the plan and carrying the interventions to resolve client’s problem. The interventions include all those independent, dependent and interdependent nursing actions carried out by the nurse to restore health, prevent illness, promote wellness and facilitate copying with altered functioning. The implementation of nursing action is followed by complete and accurate documentation of events.
To implement nursing care plan successfully, nurse need to have following skills-
- Cognitive skills-Including problem solving and decision making
- Interpersonal skills- include verbal and non- verbal response, communication
- Technical skills- include hand on skills need to perform procedures such as administrating injection, drugs, lifting, moving.
- Legal skills- Ethically and legally skilled nurse conduct themselves as effective patient advocate, practice nursing as per code of ethics and appropriate standards of practice, use legal safeguards that reduce the risk of litigation.
Process of Implementation-
- Reassessing the client
- Setting priorities
- Performing nursing intervention
- Delegating and Supervising
- Recording nursing actions
1. Reassessing the client-
- Just before implementation the nurse must reassess whethe the intervention is still needed because a client's condition can change quickly and dramatically.
Example- The client who experience pain may become quiet and withdraw free external stimuli.
- Assessing the client is carried out throughout the nursing process. As they initiate the nursing plan of care a nurse must ensure that the planned interventions are still relevants
2. Setting Priorities- When a person's condition change priorities also change.Priorities are based on information collected during caring reassessment. When setting priorities a nurse must rank nursing problems based on several factor-
- The client's condition.
- New information from reassessment.
- Time and resource available.
- Feedback from client, family and health staff
- The nurse's experience in assessing situation.
3. Perform Nursing Interventions-
- Nurse carry out the nursing intervention listed on the nursing plan of care. If a nurse is caring for several client's he or she develops schedule so that all clients are cared in a timely fashion.
4. Delegating and Supervising-
There are two responsibilities the nurse should do while making work assignments.
- Make a appropriate delegation of duties.
- Make adequate supervision of personal.
5. Recording Nursing Action-
- After carryout nursing interventions, a nurse record them in the client's health record. Each institution determines the specific requiremett for documentation and should prepare written guidelines for the use of all forms.
E. Evaluation-
Evaluation is used to judge each component of nursing process. It measures the effectiveness of nursing interventions. It consists of comparing and judging the data about client’s progress. The client’s response to the nursing interventions will guide the nurse to continue with the plan care, modify it or terminate. In case the plan of care needs modification the nurse will reassess and carry out the remaining steps of nursing process. When the care is continued the ongoing process of assessment and evaluation is continued.
Purposes-
- To collect the objective and subjective data to make judgments about nursing care delivered.
- To examine the client's behavioral responses to nursing interventions.
- To compare the client's behavioral response with predetermined outcome criteria.
- To appraise the extent to which client goals were attained or problem resolved.
Types of Evaluation
1. Structure Evaluation-
- Structure evaluation focus as on the setting where healthcare is provided. It deals with the environmental aspects that directly or indirectly influences the quality of care provided.
- Availability of equipment, layout of physical facilities, nurse client ratio, administrative support and maintenance of nursing staff all are together structure as evaluation.
2. Process Evaluation-
- Process evaluations focuses on the nurse's performance. The phases of the nursing process are used as the framework for the evaluation of nursing care.
3. Outcome Evaluation-
- Outcome evaluation, which focuses on the client.
- Outcome evaluation can take place only after standards have been developed.
Evaluation Process/Components of Evaluation-
- Collection data
- Comparing collected data with desired outcome.
- Analyzing client's response related to nursing activities.
- Identifying factors that contributed to the failure of the care plan.
- Continuing, modifying or terminating the nursing care plan.
1. Collecting Data-
- Systematic data collection is required to determine goal achievement Subjective data are collected from any source: the client, family members or others Objective data are collected from observer, health records, physical assessment and measurement devices, all data are evaluate the effectiveness of nursing care provided.
2. Comparing collected data with desired outcome-
- After collecting data, nurse compares the data with desired outcome by client's behavioral response to nursing intervention judgment of desired outcome by comparing the client's actual behavioral in response to the predicted response or predetermined outer criteria developed in the planning phase.
3. Analyzing client's response related to nursing activities-
- Analyzing the client's response related to nursing activities by the recollection of data.
Example:- Client will state that the pain is relieved within 10 min. after repositioning. The client's subjective statement would be needed to judge whether this goal has been achieved or not.
4. Identifying factors that contributing to the failure to the care plan-
Several factors to goal attainment have been identified. Barriers may involve the client, family members or other some factor are-
- Neglecting to collect pertinent assessment data, delegating nursing care to inappropriate nursing staff members.
- Lack of communication among the health care team.
- Lack of understanding the plan of care
-
Lack of interest in the client.
-
Having an unexpected reaction to treatment.
5. Continuing, modifying or terminating the nursing care plan-
- Continuing and modifying of the nursing plan of care is a part of evaluation phase. It provides best care to client. Nursing diagnosis that are resolved required no further nursing intervention and may be removed or terminated from the nursing plan of care. The levels of functioning and health status changes are periodically reassessed to determine whether new problems or nursing diagnosis have developed.
While documenting evaluating phase, the nurse can draw one of the three possible conclusion-
- The goal was met-The client response is the same as the desire outcomes.
- The goal was partially met- Either a short term goal was achieved but the long term was not, or the desire outcome was only partially attained.
- The goal was not met